Production strategies
Production strategies can be divided into three main categories:
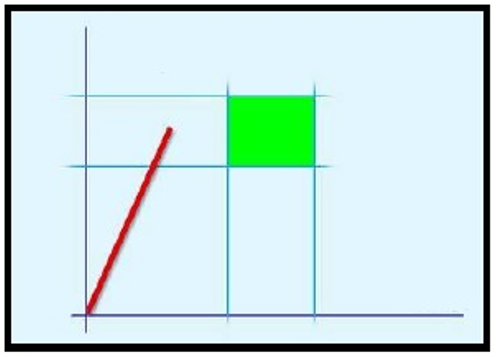
Tightening within torque limits: this is the easiest tightening method, it is enough applying torque within the limits.

Torque vs. Time A
Upper torque limit
B
Nominal
C
Lower torque limit
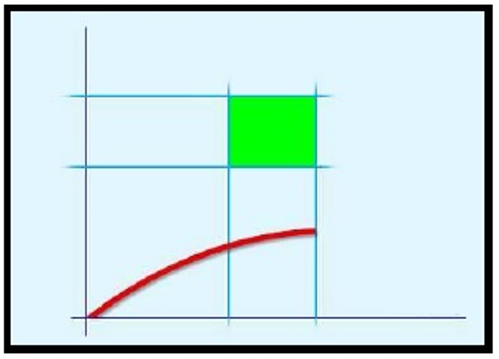
Tightening within torque and angle limits: this is a more reliable way to tighten, because an additional information (angle) is used during the tightening process.
Torque vs. Angle A
Upper torque limit
B
Nominal
C
Lower torque limit
D
Lower angle limit
E
Upper angle limit
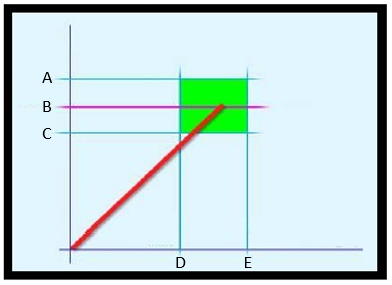
Using this method, it is possible to detect potential problems on the joint (refer to the following examples):
Torque is correct, but angle is too small:
|
|
|
|
Tightening with torque and additional angle rotation (torque + angle): the bolt is first tightened to a certain torque and then it is further tightened to a specific angle. The goal is to stress the bolt over the yield point. Even with differences in the angle, the torque (causing clamping force) is quite reliable. Sometimes the joint is specially designed and the analysis of the joint helps making sure that strain is far away from the breaking point.

Torque vs. Angle Tightening to elastic limits (yield) : The bolt is tightened until its elastic limit is reached. This method is used when each bolt must achieve the maximum clamping force. This method is seldom used in the car industry (example: Connecting rods). It is more common in the aerospace industry.

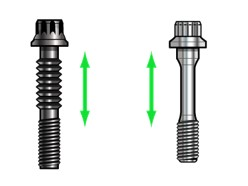 | These bolts are normally used in special applications and the shank of the bolt is designed with a special thin section to be stretched (this bolt works as a precise spring). |