Torcflex Low Profile Tool
Hydraulic Torque Wrench
Product Information
General Information
Safety Signal Words
The safety signal words Danger, Warning, Caution, and Notice have the following meanings:
DANGER | DANGER indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. |
WARNING | WARNING indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury. |
CAUTION | CAUTION, used with the safety alert symbol, indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury. |
NOTICE | NOTICE is used to address practices not related to personal injury. |
Warranty
Product warranty will expire 12+1 months after dispatch from Atlas Copco's Distribution Center.
Normal wear and tear on parts is not included within the warranty.
Normal wear and tear is that which requires a part change or other adjustment/overhaul during standard tools maintenance typical for that period (expressed in time, operation hours or otherwise).
The product warranty relies on the correct use, maintenance, and repair of the tool and its component parts.
Damage to parts that occurs as a result of inadequate maintenance or performed by parties other than Atlas Copco or their Certified Service Partners during the warranty period is not covered by the warranty.
To avoid damage or destruction of tool parts, service the tool according to the recommended maintenance schedules and follow the correct instructions.
Warranty repairs are only performed in Atlas Copco workshops or by Certified Service Partners.
Atlas Copco offers extended warranty and state of the art preventive maintenance through its ToolCover contracts. For further information contact your local Service representative.
Website
Information concerning our Products, Accessories, Spare Parts and Published Matters can be found on the Atlas Copco website.
Please visit: www.atlascopco.com.
ServAid
ServAid is a portal that is continuously updated and contains Technical Information, such as:
Regulatory and Safety Information
Technical Data
Installation, Operation and Service Instructions
Spare Parts Lists
Accessories
Dimensional Drawings
Please visit: https://servaid.atlascopco.com.
For further Technical Information, please contact your local Atlas Copco representative.
Safety Data Sheets MSDS/SDS
The Safety Data Sheets describe the chemical products sold by Atlas Copco.
Please consult the Atlas Copco website for more information www.atlascopco.com/sds.
Safety Warning
 Do not modify or subject any equipment or accessories to impact - Contact Atlas Copco for special tool applications or equipment modifications. Unauthorized modifications may lead to premature tool failure which may cause injury.
Do not modify or subject any equipment or accessories to impact - Contact Atlas Copco for special tool applications or equipment modifications. Unauthorized modifications may lead to premature tool failure which may cause injury.
 Do not use electric pump in explosive or wet environment - If electric pump is used, ensure that extension cable, power supply and earthing meet electrical code. Be aware of electrical hazards, e.g. sparking and shocks.
Do not use electric pump in explosive or wet environment - If electric pump is used, ensure that extension cable, power supply and earthing meet electrical code. Be aware of electrical hazards, e.g. sparking and shocks.
 High hydraulic pressure hazards -
High hydraulic pressure hazards -
Use correct tools, hoses and fittings. Ensure all hose connections are fully connected, tight and leak free.
Keep clear off leaking hydraulic fluid. Clean any spillages.
Never exceed the maximum working pressure of the pump. Ensure hose and fittings are rated for 10000 psi (700 bar) dynamic working pressure. The maximum working pressure is permanently marked on the tool.
 Keep hands and fingers clear from pinch points - Pinch points exist around reaction area and when operating in tight spaces.
Keep hands and fingers clear from pinch points - Pinch points exist around reaction area and when operating in tight spaces.
 Maintain equipment in good working order - Inspect for tool damage, cracks or wear and lubricate in line with equipment usage. Remove damaged equipment from service.
Maintain equipment in good working order - Inspect for tool damage, cracks or wear and lubricate in line with equipment usage. Remove damaged equipment from service.
 One Person operation recommended - Only trained and competent personnel should control the operation of the tool. When two person tool operation cannot be avoided, a risk assessment must be performed that fully addresses the environment, application, co-ordination (between operators) and communication. The operator holding the torque wrench should control operations, i.e. the person in control does not necessarily have the control pendant in his possession, however they will give the commands to energize the pump/tool.
One Person operation recommended - Only trained and competent personnel should control the operation of the tool. When two person tool operation cannot be avoided, a risk assessment must be performed that fully addresses the environment, application, co-ordination (between operators) and communication. The operator holding the torque wrench should control operations, i.e. the person in control does not necessarily have the control pendant in his possession, however they will give the commands to energize the pump/tool.
 Set tool reaction correctly - Incorrect or unstable reaction point may cause tool to move during operation, increasing operator risk. Poor reaction point selection may also lead to premature tool failure.
Set tool reaction correctly - Incorrect or unstable reaction point may cause tool to move during operation, increasing operator risk. Poor reaction point selection may also lead to premature tool failure.
 Wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment - Suitable for working with or close to high pressure hydraulic systems, e.g. Safety Glasses (EN166), Gloves, Safety footwear etc. Do not wear loose fitting gloves or gloves with cut or frayed fingers. Gloves can become entangled with the rotating drive/socket causing severed or broken fingers.
Wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment - Suitable for working with or close to high pressure hydraulic systems, e.g. Safety Glasses (EN166), Gloves, Safety footwear etc. Do not wear loose fitting gloves or gloves with cut or frayed fingers. Gloves can become entangled with the rotating drive/socket causing severed or broken fingers.
 Do not expose hoses to excessive bending, ensure hoses do not become trapped or damaged - Hose damage can result from thermal, mechanical or chemical abuse; causing the release of high pressure hydraulic fluid which may result in equipment damage and personal injury.
Do not expose hoses to excessive bending, ensure hoses do not become trapped or damaged - Hose damage can result from thermal, mechanical or chemical abuse; causing the release of high pressure hydraulic fluid which may result in equipment damage and personal injury.
 Tool Selection - Select appropriate tool for the application based upon torque requirements and space constraints.
Tool Selection - Select appropriate tool for the application based upon torque requirements and space constraints.
Country of Origin
For the Country of Origin, please refer to the information on the product label.
Dimensional Drawings
Dimensional Drawings can be found either in the Dimensional Drawings Archive, or on ServAid.
Please visit: https://webbox.atlascopco.com/webbox/dimdrw or https://servaid.atlascopco.com.
Overview
Low Profile Wrench Overview
The Torcflex low profile wrench (TFX) is a professional hydraulic power tool that is designed to exert torque on industrial fasteners to make sure of correct tightening or loosening of an industrial bolted connection. The tool uses a double acting hydraulic cylinder to transfer linear force into rotation torque through a ratchet mechanism. The torque is controlled by adjusting the pressure applied to the hydraulic cylinder.
The tool includes the following main components:

A | Swivel manifold | A swivel manifold with hydraulic couplings to allow connection to an appropriate hydraulic power supply. |
B | Ratchet link | A ratchet link which provides the hexagonal drive. Atlas Copco provides several optional ratchet links for each powerhead model, so the hexagon size can be changed. |
C | Hexagon drive | The hexagon drive is the functional part to apply torque for the ratchet link. |
D | Retained pin | A retained pin for connecting the powerhead to the ratchet link. |
E | Reaction arm | A fixed reaction arm to absorb the reaction force generated during tool operation. |
F | Powerhead | A powerhead which is the hydraulic element of the tool. |
Technical Data
Power Supply Hydraulic Pressure All Models
Min 104 bar – Max 700 bar Min 1500 psi – Max 10000 psi |
Product No. | Torque Range Min. | Torque Range Max. | Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Nm | ft lb | Nm | ft lb | kg | lb | |
Powerhead, TFX02 (Twin) 8434241975 | 348 | 257 | 2318 | 1710 | 1.31 | 2.89 |
Powerhead, TFX02 (Co-Axial) 8434240668 | 348 | 257 | 2318 | 1710 | 1.12 | 2.47 |
Powerhead, TFX04 (Twin) 8434241976 | 784 | 579 | 5227 | 3855 | 2.14 | 4.72 |
Powerhead, TFX04 (Co-Axial) 8434241147 | 784 | 579 | 5227 | 3855 | 1.96 | 4.32 |
Powerhead, TFX08 (Twin) 8434242070 | 1658 | 1223 | 11051 | 8151 | 3.46 | 7.63 |
Powerhead, TFX08 (Co-Axial) 8434241787 | 1658 | 1223 | 11051 | 8151 | 3.29 | 7.25 |
Powerhead, TFX14 (Twin) 8434242405 | 2725 | 2010 | 18168 | 13400 | 5.27 | 11.62 |
Powerhead, TFX14 (Co-axial) 8434242402 | 2725 | 2010 | 18168 | 13400 | 5.1 | 11.24 |
Powerhead, TFX18 (Twin) 8434242732 | 3879 | 2861 | 25861 | 19074 | 7.08 | 15.61 |
Powerhead, TFX18 (Co-axial) 8434242713 | 3879 | 2861 | 25861 | 19074 | 6.92 | 15.26 |
Powerhead, TFX30 (Twin) 8434242734 | 6467 | 4770 | 43115 | 31800 | 11.55 | 25.47 |
Powerhead, TFX30 (Co-axial) 8434242733 | 6467 | 4770 | 43115 | 31800 | 11.38 | 25.08 |
Dimensions
Dimensional Drawings can be found either in the Dimensional Drawings Archive, or on ServAid: https://webbox.atlascopco.com/webbox/dimdrw or https://servaid.atlascopco.com.
Technical Product Data
Technical Product Data can be found on either ServAid, or the Atlas Copco website.
Please visit: https://servaid.atlascopco.com or www.atlascopco.com.
ATEX Certification Information
ATEX
Only tools and equipment correctly certified and marked with ATEX symbol should be utilized in potential explosive zones.

Operator must read and understand all operating instructions prior to use!
This (additional) information and guidance must be used in conjunction with the Standard Product and Safety Instructions supplied with all Torcflex hydraulic torque wrenches.
ATEX Zone Operation: Additional care and attention should be applied when working within potentially explosive environments. Special consideration is required with respect to the tightening application and use of the Torcflex range of tools, the operator must perform a risk assessment prior to the use of any Torcflex hydraulic torque wrench within a potentially explosive (ATEX zoned) environment.
It is the operators’ responsibility to maintain the tool to ensure its safe operation within ATEX rated zones. Failure to comply with the maintenance recommendations will increase the likelihood of mechanical failure and therefore the chance of mechanical spark generation.
If the wrench shows any sign of malfunction, remove it from the ATEX zone before investigating the cause. DO NOT attempt to repair the wrench in the ATEX zone.
If the wrench is dropped, remove it from the ATEX zone before looking for damage. Do a pressure test and functional test before using it again.
Torcflex Wrench Inspection
Inspect the general condition of the Torcflex wrench before using the tool in an ATEX zone. Particular attention should be given to the drive components, i.e., the square or hexagon drive, ratchet, and drive pawls. Any parts that are in poor condition or that have had significant use must be replaced. During re-assembly, ensure that the parts are correctly lubricated in accordance with maintenance instructions.
System and Operational Considerations
Only use Torcflex torque wrenches in ATEX zones when connected with/to other ATEX declared or certified components, e.g., hoses and hydraulic pump.
Confirm electrical continuity through the torque wrench system. To prevent any static build up, suitably earth / electrically ground the system / pump.
Additional care should be taken when selecting reaction points and in the placement and support of the hydraulic torque wrench.
Ensure accessories and sockets used are in good operational order and suitable for use within potentially explosive atmospheres.
ATEX Code Definition
The ATEX code is: | |
|---|---|
II 2 G Ex h IIC T4 Gb II 2 D Ex h IIIC T135°C Db -20°C ≤ Ta ≤ 40°C | |
Description | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
Equipment group | II | Surface industry |
Equipment category Group II | 2 | High level of protection
|
Atmosphere
| G | Atmosphere containing Gas, Vapors or Mist |
D | Atmosphere containing Dust | |
Safety design | h | Mechanical product |
Gas group | IIC | Hydrogene/ Acetylene |
IIB | Ethylene | |
Dust group | IIIC | Surface combustible dust |
Max surface temperature in Gas atmosphere |
| T1 = 450°C T2 = 300°C T3 = 200°C T4 = 135°C T5 = 100°C T6 = 85°C |
Max surface temperature in Dust atmosphere |
| Example temperatures: T85°C T100°C T135°C T200°C T240°C |
Installation
Installation Requirements
General Installation Requirements
To operate Torcflex wrenches, connect the wrench to a hydraulic power pack with a hydraulic hose. For maximum efficiency and accuracy, use Atlas Copco torque wrench pumps and hoses. If Atlas Copco pumps and hoses are not used, make sure of the following before connecting Torcflex wrenches:
System requirements:
All system components must have a dynamic pressure rating of 700 bar (10,000 psi).
Pump requirements:
Maximum Advance Pressure: 700 bar (10,000 psi).
Maximum Retract Pressure: 120 bar (1,740 psi).
Remote-operated directional control valve for operating the double acting cylinder; the pressure must be released when switching between Advance and Retract.
For safety, the remote must be configured to automatically retract the tool if the button is released.
Adjustable pressure relief valve.
Calibrated pressure gauge (Class 1 Accuracy).
For screw-to-connect coupling systems, make sure that the Advance coupling is male and the Retract coupling is female. For more information, refer to section Connecting the System - Screw-to-Connect Coupling.
Torcflex wrenches fitted with screw-to-connect couplings use CEJN 232 couplings with ¼ NPT threads. Before using alternative brand couplings in the system, verify the compatibility. For more information, refer to section Connecting the System - Screw-to-Connect Coupling.
Hydraulic hose requirements:
Advance line − female to female coupling.
Retract line − male to male nipple.
Before connecting the system, do the following:
On electric pumps, make sure that the power supply is appropriate for the pump and minimize the length of extension cords.
On pneumatic pumps, make sure that the air supply is appropriate for the pump and minimize the length of air lines.
Look for any damage on the power and pendant cables before connecting the cables to the power supply.
Look for any damage on the hydraulic hoses and couplings before connecting the hoses to the system.
Inspect the oil level and fill if necessary.
Make sure that the pressure gauge is calibrated.
Make sure that the impact sockets are the correct size for the application.
Make sure that the impact sockets are free from damage.
Select a wrench based on the target torque for the application.
To prolong the lifespan of the wrench, do not operate the tool above 80% capacity for long periods. As with any machine, operating it continuously at maximum capacity will reduce its lifespan. It will also need maintenance and replacement of worn parts more often.
For applications where the back nut can rotate, make sure that a suitable backup wrench is available.
Installation Instructions
Installing the TL Ratchet Link
Make sure that the piston rod end and drive plates are lubricated properly before installation.

Inserting the Ratchet Link
Pull out the link pin (1). Push the ratchet mechanism (2) all the way in, and hook the powerhead to the link.
Secure the powerhead with the link pin (3).

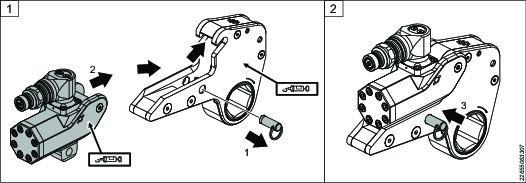
Installing the RL Ratchet Link
Make sure that the piston rod end and drive plates are lubricated properly before installation.

Inserting the Ratchet Link
Pull out the link pin (1). Push the ratchet mechanism (2) all the way in, and hook the powerhead to the link.
Secure the powerhead with the link pin (3).
Installing the Support Handle
Make sure that the handle has the correct bolt size before you install the handle onto the wrench. Two support handle screw sizes are available; select the correct bolt size from the list.
TF01 / TFX02 = M6
TF03/05/08/10 / TFX04/08/14/18/30 = M8
The wrench supports the installation of the support handle at three different positions.
Side positions, left or right:

Front position:

Powerhead side position, left or right:

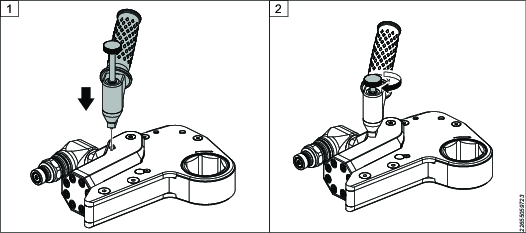
Preparing the Handle for Installation
Insert the bolt through the handle.
Screw the bolt into place with the thumbscrew.
Make sure that the bolt has axial float to allow installation.

Installing the Handle on the Wrench
Insert the dowel pins on the base of the handle into the holes on the wrench.
Hold the handle in place and screw the bolt into the wrench with the thumb screw until tight.
Adjusting the Handle Position
The bolt does not need to be loosened to adjust the handle position.
You can turn the support handle to 12 positions in 30-degree increments:
Pull and hold the ring pin.
Rotate the handle to the desired position and release the ring pin to lock.

Releasing the Pressure
Torcflex wrenches can be supplied with either co-axial couplings or screw-to-connect couplings. The co-axial coupling system connects both the advance line and retract line with a single connection. The screw-to-connect coupling system requires the advance and retract lines to be connected individually. Before connecting, make sure that the couplings are clean and free of damage.
Before you try to connect or disconnect hydraulic couplings, make sure that there is no residual pressure in the pump.
Electric Pumps
Press the button on top of the solenoid valve several times to release the pressure.

Pneumatic Pumps
Press the Stop [0] button on the remote control pendant to stop the pump.
Press and hold the Stop [0] button and press the Advance [1] button several times to cycle the solenoid valve.
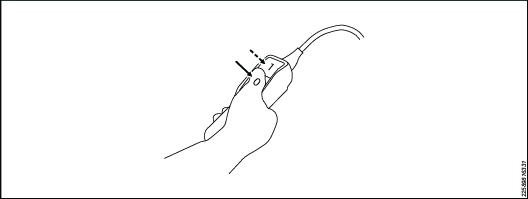
1
Advance button
0
Stop button
All couplings should be easily connected and disconnected by hand. If not, look for damage or residual pressure in the system.
Connecting the System - Co-axial Coupling
The co-axial system connects both the advance and retract lines of the hydraulic circuit using a single coupling.

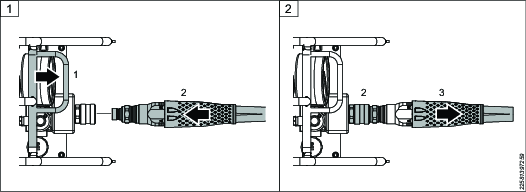
Connecting the Hose to the Pump
Hold the pump frame (1) to prevent the pump from moving during the connection. Position the hose nipple (2) in line with the pump coupling.
Firmly push the hose nipple and pump coupling together (2). A click is heard when the connection is complete.

The knurled collar on the pump coupling does not need to be drawn back during the connection.
Pull the hose (3) to make sure that the connection is correct.
Connecting the Hose to the Wrench
Support the swivel manifold at the opposite side to the coupling (1). Position the hose coupling in line with the wrench nipple (2).
Firmly push the wrench nipple and hose coupling together. A click is heard when the connection is complete.

The knurled collar on the hose coupling does not need to be drawn back during the connection.
Pull the hose (3) to make sure that the connection is correct.
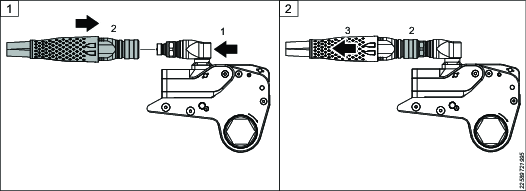
Disconnecting the Hose from the Pump
The co-axial coupling has a safety feature to prevent accidental disconnection during use. Learn how to disconnect the hose before using the equipment.
Hold the pump frame to prevent the pump from moving during the disconnection.
Push the hose nipple towards the pump (illustration 1) until the gap between the knurled collar and the nipple closes (illustration 2).
While holding the above position, push the knurled collar towards the pump (Illustration 3).
Pull the hose away from the pump and the connection will automatically spring apart (illustration 4).
If the connections are not pushed together and held, the knurled collar cannot move, therefore the couplings cannot be disconnected. This is a safety feature to prevent accidental disconnection.


Disconnecting the Hose from the Wrench
The co-axial coupling has a safety feature to prevent accidental disconnection during use. Learn how to disconnect the hose before using the equipment.
Support the swivel manifold at the opposite side to the coupling.
Push the hose towards the wrench (illustration 1) until the gap between the knurled collar and the nipple closes, as shown in (illustration 2).
While holding the above position, pull the knurled collar away from the wrench (illustration 3).
Pull the hose away from the wrench and the connection will automatically spring apart (illustration 4).
If the connections are not pushed together and held, the knurled collar cannot move, therefore the couplings cannot be disconnected. This is a safety feature to prevent accidental disconnection.
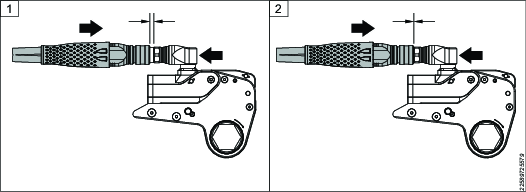

Connecting the System - Screw-to-Connect Coupling
Atlas Copco pumps and hoses have the couplings pre-configured to operate Torcflex wrenches as shown below.
If you use non-Atlas Copco equipment to operate Torcflex wrenches, make sure that the couplings are configured as shown.

1 | Wrench | 2 | Pump |
Make sure that all couplings are connected properly with no gaps between the collars and the fittings. Never use wrenches or other tools to tighten or loosen couplers.

Make sure that the connectors are fully engaged and screwed tightly together.
Never use two twin hydraulic hoses between the pump and the tool. To avoid tool malfunction, do not reverse the connectors. Do not try to tighten or loosen any couplings under pressure.
Operation
Ergonomic Guidelines
Consider this list of general ergonomic guidelines to identify areas for improvement in posture, handling or work environment.
Take frequent breaks and change work positions frequently.
Adapt the workstation area to your needs and the work task.
Adjust for a convenient reach range by determining where tools need to be located to avoid static load.
Avoid work positions above shoulder level or with static holding during assembly operations.
When working above shoulder level, reduce the load on the static muscles by lowering the weight of the tool, using for example torque arms, hose reels or weight balancers. You can also reduce the load on the static muscles by holding the tool close to the body.
Take frequent breaks.
Avoid extreme arm or wrist postures, particularly during operations requiring a degree of force.
Adjust for a convenient field of vision that requires minimal eye and head movements.
Use appropriate lighting for the work task.
Select the appropriate tool for the work task.
In noisy environments, use ear protection equipment.
Operating Instructions
Operation Safety
Working Pressure
All system components must have a dynamic pressure rating of 700 bar (10,000 psi). If other than Atlas Copco pumps and hoses are used, make sure that the equipment is suitable for use with Atlas Copco wrenches.
Pump Working Pressure:
Maximum Advance Pressure: 700 bar (10,000 psi)
Maximum Retract Pressure: 120 bar (1,740 psi)
Setting the Target Torque
Once the wrench is set up and connected to a pump, you must set the target torque output. To set the torque output, you must adjust the pressure output value at the pump.
Look at the calibration data sheet or the torque/pressure conversion chart for the tool to determine the pressure that will deliver the correct torque.
Loosen the lock nut on the pressure regulating valve, then loosen the thumbscrew until it is turning freely. Do not remove the thumbscrew.
Connect the pump to a suitable power supply.
With the wrench free to move, that is, not applied on a fastener, start the pump by pressing and releasing the Advance button [1] on the remote control pendant once.
Press and hold the Advance button [1].
The wrench piston advances to full stroke and the pressure builds up.
Monitor the pressure displayed on the gauge. Continue to hold the Advance button [1] and tighten or loosen the thumbscrew until the gauge reaches the target value.
Release the Advance button [1].
The wrench piston retracts.
Press and hold the Advance button [1] again. Make sure that you get the target value, then release the Advance button [1].
Hold the thumbscrew in position and lock the valve with the lock nut.
After locking the valve, press and hold the Advance button [1] once more and make sure that you still get the target value. Adjust if necessary.
The system is now ready for use.
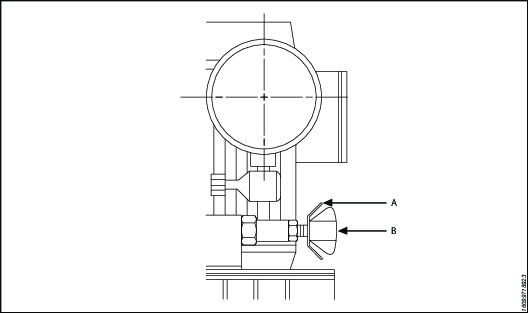
A | Knurled lock nut | B | T-handle |

1 | Advance button | 0 | Stop button |
Operating the Low Profile Wrench
Prerequisites
Wear personal protective equipment: Correct and appropriate safety equipment must be worn.
Always perform a task-based risk assessment before using the tool.
Frequently inspect the tool, power pack, hoses, connectors, electric cables, and accessories for visible damage. Always follow instructions for tool and pump maintenance.
Select the appropriate size low clearance ratchet link and insert it into the tool. Tool operation, bolt tightening and loosening, is determined by the position of the tool relative to the nut/bolt.
Connect the hoses: Make sure that all hose connections are secure and correctly made. Make sure that the hoses are free from defects.
Start up
Cycle the tool: Place the tool on a flat surface, turn the pump on. Press and hold the Advance [1] button on the pump remote control pendant until the tool clicks. Release the button, wait for the tool to click. Repeat.
Set the pressure: Press and hold the Advance [1] button and slowly turn the pressure regulator clockwise to reach the correct pressure.
Place the tool on the nut to be tightened or loosened.
The driving stroke of the power head will always turn the hex ratchet (and therefore the nut) towards the shroud at the front of the tool, that is, turning away from the reaction point. The low clearance ratchet links are supplied complete with a long reaction block. This reaction block is designed to react against an adjacent nut.
The ratchet link has been designed so that the reaction block reacts against an adjacent nut or other suitable secure reaction point. If such a reaction point is not available, standard reaction accessories are available, or if necessary, special reaction arms can be supplied.
Make sure that the nut corresponds with the tool size.
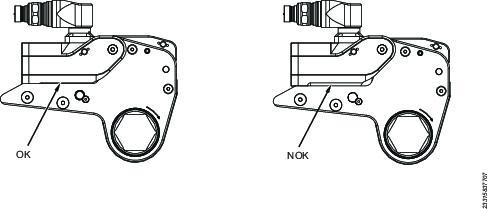
Always make sure to use a solid reaction point during operation.
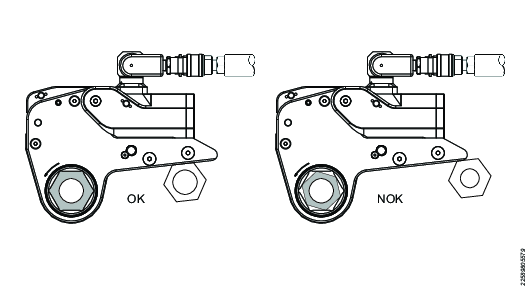
Never kink or bend hoses excessively:
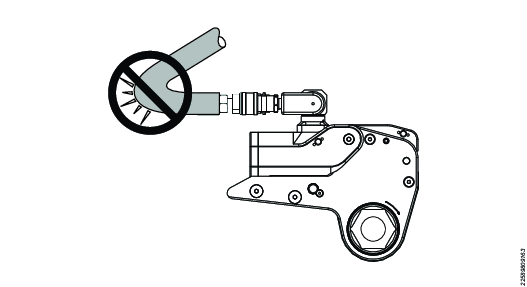
Never strike wrench to assist breakout:

Checking the Drive Direction
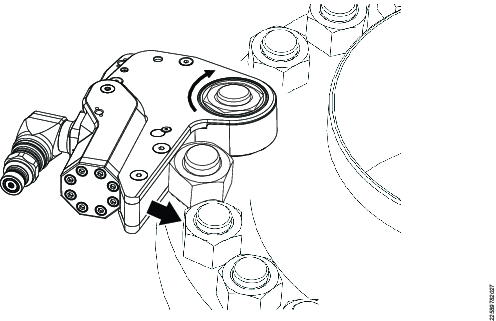
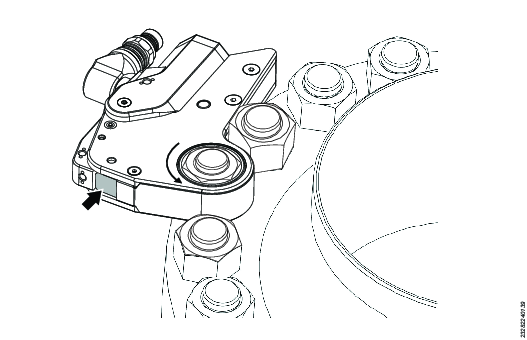
Before you use the wrench, make sure that the direction of rotation is correct. The direction is indicated by the arrow on top of the tool.
The reaction arm will rotate in the opposite direction to the drive until it contacts a suitable reaction point.

1 | Loosen: counterclockwise Tighten: clockwise |
2 | Reaction arm |
3 | Direction arrow |
If the direction of rotation needs to be reversed, turn the wrench over and install it on the application.
Tightening
Put the tool on the fastener to be tightened. Push the tool towards the reaction surface until the reaction arm contacts with a suitable reaction point.

The reaction structure must be rigid enough to withstand the reaction force from the hydraulic tool.
Avoid tapered surfaces as the reaction arm could slide, causing adverse loading and tool instability.
Do not use loose spacers to create a reaction structure. If the standard reaction arm is not suitable, contact Atlas Copco for advice.
Press and release the Advance button [1] on the remote control pendant to start the pump.
Support the tool with the support handle and make sure of the following:
The ratchet link is fully engaged with the fastener being tightened.
The reaction arm is firmly against the reaction structure.
The hose and couplings are free to move, clear of surrounding structures.

Be aware that when the tool is retracting, you must support the weight of the tool; especially on inverted applications. If the tool is not supported, it can fall from the application.
Press and hold the Advance button [1] so that the drive rotates.
When the piston reaches the end of the stroke, the following happens:
The reaction pawl makes a click sound.
The ratchet link stops turning.
The pressure builds up to the set pressure value.
This does not mean that the bolt is tightened correctly, it only indicates that the tool is at full stroke.
When the tool reaches full stroke, support the tool and release the Advance button [1] on the remote control pendant. The tool automatically retracts. When the tool is fully retracted, the drive pawl clicks.
The tool is now ready to advance again. Repeat steps 3–5 until the pressure builds directly to the target value and no movement of the fastener is observed. The wrench has stalled and the fastener is tightened correctly.
Once the tool has stalled, press the Advance button [1] once more to make sure that the fastener is not moving. If not, the tightening process is complete.
Occasionally, the tool can lock itself on the application. To remove the tool do the following:
Press and hold the Advance button [1].
Once the pressure reaches the target value, push the pawl levers by hand to disengage the pawl from the ratchet.
Support the weight of the tool before releasing the Advance button on the remote control pendant.
Remove the tool from the application.

Move the pawl levers by hand. Do not use tools to move the levers.
Press the Stop button [0] on the remote control pendant to stop the pump.
Loosening
If the fasteners are heavily corroded or have been subject to high temperature in service, the break loose torque can be more than double that of the tightening torque. Use a larger tool for loosening than for tightening. To make loosening easier, remove all surface rust with a wire brush and apply releasing oil to the nut, bolt, and bearing surface. Allow sufficient time for the oil to soak in and penetrate before trying to loosen the fastener.
When loosening fasteners, there can be a sudden release of energy when the fastener breaks free. This can cause an unexpected shock force on the tool. To protect the drive components, do not exceed 90% of maximum pressure during loosening. If 90% does not loosen the fastener, use a larger tool if possible.
Never strike a wrench or socket with a hammer to assist loosening operations.

Set the pressure target value to 620 bar (9,000 psi).
Put the tool on the fastener to be loosened. Push the tool towards the reaction surface until the reaction arm contacts with a suitable reaction point.

The reaction structure must be rigid enough to withstand the reaction force from the hydraulic tool.
Avoid tapered surfaces as the reaction arm could slide, causing adverse loading and tool instability.
Do not use loose spacers to create a reaction structure. If the standard reaction arm is not suitable, contact Atlas Copco for advice.
Press and release the Advance button [1] to start the pump.
Support the tool with the support handle and make sure of the following:
The ratchet link is fully engaged with the fastener being loosened.
The reaction arm is firmly against the reaction structure.
The hose and couplings are clear of surrounding structures and are free to move.

Be aware that when the tool is retracting, you must support the weight of the tool; especially on inverted applications. If the tool is not supported, it can fall from the application.
Press and hold the Advance button [1] so that the drive rotates.
The pressure will build until the break loose torque is achieved; then the pressure will drop as the drive rotates and the fastener loosens.
When the piston reaches the end of the stroke the following happens:
The reaction pawl makes a click sound.
The ratchet link stops turning.
The pressure builds up to the set target value.
This does not mean that the bolt is fully loosened, it only indicates that the tool is at full stroke.
When the tool reaches full stroke, support the tool and release the Advance button [1] on the remote control pendant. The tool automatically retracts. When the tool is fully retracted, the drive pawl will click.
The tool is now ready to advance again. Repeat steps 4–6 until the fastener is fully loosened.
Press the Stop button [0] on the remote control pendant to stop the pump.
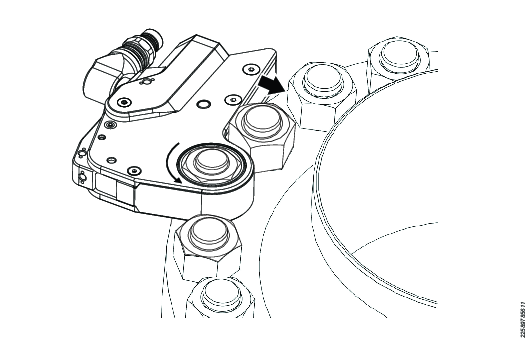
Service
Maintenance Instructions
Service and Maintenance Recommendations
Always wear impact-resistant eye and face protection when involved with or near the operation, repair or maintenance of the tool or changing accessories on the tool.
All investigation, maintenance or repair work should only be carried out when the complete system is at zero pressure.
For optimum performance, frequently inspect tool, power pack, hoses, connectors, electric cables, and accessories for visual damage. Always follow instructions for tool and pump maintenance.
Service Interval Guidance
Trained personnel with correct maintenance schedule can use hydraulic wrenches for many years without problems. However, all tools wear out after long use. Factors that affect the life of tool:
High cycle rate
High load use
Impact
Operating in dirty, hot or humid environments
Different reaction methods
Poor maintenance
Regular lubrication and overhaul is recommended to make sure that the wrench remains in good working order. More frequent service intervals may be needed if used at high torque, high cycle rate or long tightening times. If the wrench is not working properly, immediately take it away for inspection.
The following service intervals are for guidance only. Each use case and application is different, so it is the responsibility of the end user to implement suitable planned maintenance specific to the working environment and usage. Keep a record of tool operation. This record helps to plan for service, calibration, and replacement of tool or components.
Light Duty
Example: Infrequent use at low pressures, <40% capacity.
Lubrication: every 6 months
Overhaul: every 12 months
Normal Duty
Example: Regular use, <80% capacity.
Lubrication: every 3 months
Overhaul: every 12 months, including drive pin replacement. See section Lubrication.
Heavy Duty
Example: Constant use at any pressure; use >80% Capacity; regular use to loosen corroded bolts.
Lubrication: every 1 month
Overhaul: every 6 months, including drive pin and drive pawl replacement. See section Lubrication.
Use in ATEX Zones
Use the Heavy Duty guidelines regardless of duty to greatly reduce the risk of component failure when in use. If the wrench shows signs of malfunction, remove it from the ATEX zone before investigating the cause. DO NOT attempt to repair the wrench in the ATEX zone. Failure to comply with the maintenance recommendations will increase the likelihood of mechanical failure and therefore the chance of mechanical spark generation.
High Pressure Hose
Hoses should be disassembled regularly. The fittings and adaptors must be inspected for wear and damage. If wear or damage is found during maintenance, the affected part must be removed and replaced.
Examine the hoses for traces of oil that will indicate a slow leak on the hose. Pay close attention to the swages on both ends of the hose as these are the most common areas for oil leaks. If a slow leak is discovered, replace the hose.
Always clean and coil hose after every use. Wipe the hoses with a clean cloth and spray with a suitable rust inhibitor oil such as Shell Ensis or Castrol Rustillo.
Do not bend hose over obstructions or use the hose to move attached equipment.
Pressure test the hoses every second year, and replace hose sets after six years.
Tool Replacement
The product owner must implement a service plan for the tool replacement policy. This policy ensures that operating tools are replaced before the tool is no longer useful. Due to different operational environments and potential inconsistencies in tool servicing, it is difficult to define the tools lifespan.
Visual signs of wear, such as scars, dents, or missing material, indicate that the tool is no longer useful. Service tools that show signs of wear. To maintain the condition of the tools, replace any damaged parts. If the tool shows major damage to the pressure containing components or reaction arms, the correct action is to remove the tool for safety reasons.
For more information, see the Service Interval Guidance.
Preventive Maintenance
To keep the hydraulic torque wrench system in good working condition, do the following maintenance steps after each period of use.
Wipe clean all external surfaces and visually inspect the tool for signs of damage. Investigate if needed.
Examine all hydraulic joints and connections for signs of hydraulic leaks. Investigate if needed.
Make sure that all hydraulic couplings are clean and free from debris.
Inspect the full length of the hose; look for cuts or abrasions. Pay close attention to the swaged ends and look for any signs of leaks.
If the equipment is in good working order, spray with a suitable rust inhibitor oil, such as Shell Ensis or Castrol Rustillo, and store ready for next use.
Overhaul Instructions
Connect the wrench to a pump.
Pressure test to make sure that all mechanisms function as expected.
Investigate any malfunctions or hydraulic leaks.
Depressurize the system and disconnect all couplings.
Disassemble the wrench.
Replace all seals and springs.
Replace the drive pin.
Replace any other components showing signs of damage or wear.
Relubricate and reassemble the wrench.
Pressure test and make sure that all mechanisms function as expected.
Calibrate the wrench and make sure that the torque output is as expected.
Lubrication Instructions
Lubricant Guide
Drive Components | Molykote 1000 |
Seals | Rocol Sapphire Aqua-Sil |
Fasteners | Loctite 243 |
Tapered Hydraulic Threads | Loctite 577 |
Lubrication
To keep the wrenches in good working condition, lubricate the drive components periodically between service intervals.
Disassembly before lubrication:
Remove the sideplate screws and sideplate [1].
Remove the drive assembly [2].

Do the following actions during lubrication maintenance:
Examine the drive pin and springs for signs of wear or damage. Replace the drive pin and springs if necessary.
Examine the edges of ratchet teeth for signs of damage. Replace the ratchet if necessary.
Examine the drive pawl teeth for signs of damage. Replace the drive pawl if necessary.
Examine the drive pawl springs for signs of damage. Replace the springs if necessary.
Lubricate the shaded areas with Molykote 1000.
The procedure for assembly is the same as for disassembly but backwards.
Dismantling/Assembling Instructions
Disassembling the Powerhead
Loosen the swivel retaining bolts.
Remove the swivel.
Position the oil ports over a suitable container.
Pull the piston rod out until it stops.
Push the piston rod back.
The oil from the tool runs out through the ports.
Remove the endcap screws and the endcap.
Pull the piston rod out until it stops. Clamp the piston rod end in a vice.
Loosen the piston rod end with a socket and extension bar. Unscrew the piston rod end.
Withdraw the piston from the housing bore.
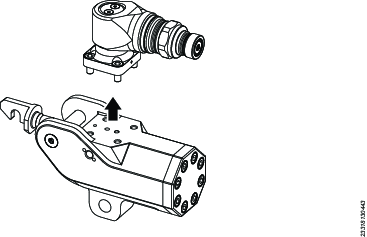

Disassembling the Ratchet Link
The procedure for disassembly is the same as for assembly, but backwards. See section Assembling the Ratchet Link.
Assembling the Powerhead
Lubricate the lip seal with Aqua-Sil and insert into the housing [1].
Lubricate the O-ring and lip seal with Aqua-Sil and install on the piston [2].
Lubricate the O-ring with Aqua-Sil and install on the end cap [3].
Apply a smear of hydraulic oil to the bore of the housing.
Insert the piston into the housing and push it to the bottom of the housing bore.
Apply Loctite 277 to the threads on the piston rod end and screw it into the piston rod.
Clamp the piston rod end in a vice and torque the piston rod using a socket and extension bar.
Model
Installation Torque (Nm)
Socket Size
TFX02
12
9/16 in.
TFX04
40
19 mm
TFX08
45
24 mm
TFX14
80
1-1/8 in.
TFX18
90
1-1/8 in.
TFX30
100
38 mm
Insert the endcap into the housing.
Apply Loctite 243 to the end cap screws; screw them into the housing and tighten to the correct installation torque.
Model
Hex Key (mm)
Torque (Nm)
TFX02
4
11
TFX04
5
18
TFX08
6
40
TFX14
8
70
TFX18
8
80
TFX30
10
125
Install the swivel manifold. See section Assembling the Swivel Manifold.
Degrease the threads on the fixed pin and apply Loctite 243 to the female thread. Screw the 2 parts of the fixed pin together and tighten to the correct installation torque.
Model
Hex Key (mm)
Torque (Nm)
TFX02
4
5
TFX04
5
8
TFX08
6
12
TFX14
6
18
TFX18
6
18
TFX30
6
18

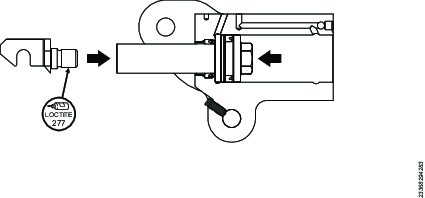

Assembling the Swivel Manifold
The Torcflex wrench can be fitted with 2 types of swivel manifold. Follow the instructions below to replace or change the manifold when needed.
Use Loctite 243 as thread locker to prevent loosening on assemblies.
Model | Hex Key (mm) | Torque (Nm) |
|---|---|---|
TFX02 | 4 | 11 |
TFX04–TFX30 | 5 | 18 |
Installing a Co-axial Swivel Manifold

Installing a Twin-line Swivel Manifold

Filling Oil
Connect the wrench to a pump with a hose.
Press and release the Advance button [1] to start the pump.
The retract side of the hydraulic cylinder is automatically filled and pushes the piston to the starting position. Air from the advance side of the piston will be forced into the hose.
Press the Stop button [0] to stop the pump. Then press the button on the directional control valve to depressurize the retract line.
Disconnect the hose and purge the air from the hose, as follows:
For co-axial hoses: With the wrench disconnected, start the pump and stop it again after 10 seconds. This will cause oil to circulate between the advance and retract lines and will purge the air out of the hose.
For screw-to-connect hoses: screw the loose ends of the hoses together to form a loop. Start the pump and stop it again after 10 seconds. This will cause oil to circulate between the advance and retract lines and will purge the air out of the hose.
Reconnect the hose to the wrench.
Advance and retract the piston 10 times.
Stop the pump.
Disconnect the hose and repeat the air purge procedure.
Pressure Testing
Connect the wrench to the pump.
Press and release the Advance [1] button to start the pump. Wait for 10 seconds and look for any signs of oil leaks.
Press and hold the Advance button and pressurize the tool to 690 bar (10,000 psi). Hold for 10 seconds and look for any signs of oil leaks.
Release the button and pressurize again 3 times, look for any signs of oil leaks each time.
Assembling the Ratchet Link
Attach the top spacer, reaction spacer, and reaction pawl pin to the sideplate with the screws. Apply Loctite 243 to the screws and torque in position.
Model
Small Screw Hex Drive
Large Screw Hex Drive
Size
Torque (Nm)
Size
Torque (Nm)
TL02
1/8 in.
6
5/32 in.
12
TL04
5/32 in.
12
3/16 in.
16
TL08
3/16 in.
16
7/32 in.
20
TL14
7/32 in.
25
5/16 in.
35
TL18
7/32 in.
40
5/16 in.
50
TL30
5/16 in.
45
3/8 in.
55
Lubricate the sideplate and the reaction pawl pin with Molykote 1000. Then assemble the shroud and reaction pawl with the spacers and the spring.
Apply Loctite 243 to the shroud screw and tighten into the reaction spacer.
Lubricate the driveplate and the bearing diameters of the ratchet with Molykote 1000. Then install on the sideplate.
Insert the ratchet through the drive plate and into the sideplate.
Put the spring pins [2×] into the drive plate.
Assemble the drive pawls [2×], spring, and spring guide.
Install the drive pin and spring.
Lubricate both sides of the second driveplate with Molykote 1000. Position the holes in line with the spring pins, then tap the spring pins into place. Make sure that the drive pawl holes remain in line.

Make sure that the gap between the driveplates is parallel and evenly spaced, and that the springs are hooked over the pin for the drive pawls to function correctly.
Test that the drive pawls function as expected: hold the ratchet and push the drive plates.
The drive pawls should both lift over the ratchet teeth and click back into place. If the drive pawls get stuck, make sure that the gap between the driveplates is correct.
Lubricate the bore and inside face of the sideplate with Molykote 1000. Put the sideplate over the ratchet and position the screw holes in line. Apply Loctite 243 to the screws and torque in position as before.
Insert the retaining pin through both sideplates. Position the pin cutout in line with the screw hole, then install the friction washer and screw. Adjust the torque on the screw to get the correct friction against the pin.






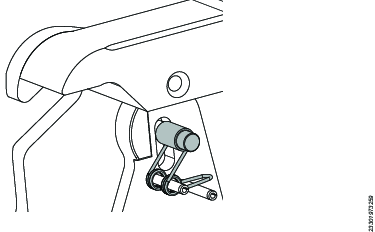




Testing the Assembly
Attach the powerhead to the ratchet link. See the section Installing the TL Ratchet Link or Installing the RL Ratchet Link, respectively.
Rotate the ratchet and make sure that the drive pawl and reaction pawls move as expected.
Connect the wrench to a pump and hose.
Advance and retract the wrench; make sure that the hexagon ratchet indexes forward with each cycle.
As a final test, calibrate the wrench to make sure that the torque output is as expected.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
Symptom | Probable Cause | Required Action |
|---|---|---|
The wrench will not advance. |
|
|
The wrench will not retract. |
|
|
The wrench will not advance but gauge shows pressure. |
|
|
The wrench operates in reverse (screw-to connect couplings only). |
|
|
Wrench pressure will not build. |
|
|
Wrench operation is slow. |
|
|
The tool is locked on the application. |
|
|
The ratchet is not taking successive strokes. |
|
|
The ratchet jumps during advance stroke. |
|
|
No reading on the pressure gauge but the wrench is operating. |
|
|
Difficult to connect the hose to the wrench or pump. |
|
|
Oil is leaking from shroud. |
|
|
The swivel or coaxial coupling is hot. |
|
|
The coupling leaks oil after disconnection. |
|
|
Recycling
Environmental Regulations
When a product has served its purpose it has to be recycled properly. Dismantle the product and recycle the components in accordance with local legislation.

