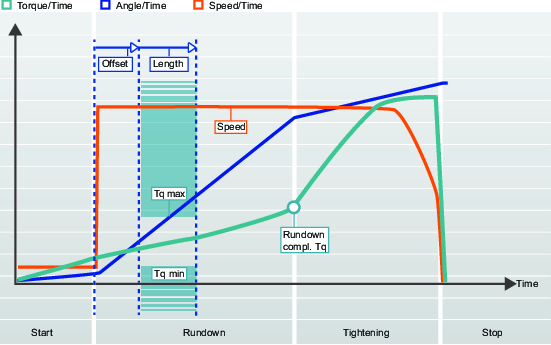
Rundown Torque Limits
The friction between the nut and joint can vary. This can cause the torque needed to run a nut down a thread, before engagement with the joint surface takes place, to vary as well. These effects could be, for example, hole interference, prevailing torque or varying lubrication.
Monitoring the rundown torque can be useful when running down a lock nut which has a plastic insert in the threads to help the fastener resist vibration. This will require a higher torque, known as prevailing torque, to overcome the interference.
Parameter | Description | Default value |
|---|---|---|
Rundown torque limits | Sets Rundown torque limits to On or Off. Off: No limits are set. On: Torque limits and angle interval are set. | Off |
Offset | Angle offset before the Angle interval begins. | 0° |
Length | Angle defining the Rundown torque limit section. | 360° |
Torque min | Torque value for lower Rundown torque limit. | 0 Nm |
Torque max | Torque value for upper Rundown torque limit. | 19% of Target torque |










































