Tells the user whether it is possible to configure the event through the "Configure Event" page.
Power Focus HC (3.10)
Software
Introduction
In this section, you can find the basic information about the product and also the formatting conventions used in the topics.
General Description
The Smart Tensioning System is a traceable and guided bolt tensioning solution which consists of three main components. The smart tensioner (STT) comes with integrated electronics and sensors, giving instant feedback to the operators. The Hand Controller (PFHC) is the brain of the system, controlling the process including; scanning with integrated barcode reader, operating the power pack and collecting data. The whole system works in a closed loop, with all commands given by the hand controller.The Power Pack comes with our heavy-duty motor and high-performance electronics.
Conventions
To enhance user understanding, certain formatting conventions are used throughout this document. The formatting conventions used are listed below.
Element | Notation | Description | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
General emphasis | In the Program workspace. | To make certain text elements stand out, or to highlight. | Text in Bold |
Graphical User Interface (GUI) items | Select the Function button. | Any reference to items found on screen in the GUI (for example, command buttons, icon names and field names). | Text in Bold |
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Path > | Generally, on the top of the GUI. | Navigation aid which keeps track of the location in the GUI. | For example: Controller > Program > Edit |
User input | Enter a Description for the program. | Any text input by the user. | Text in Bold |
File names | Enter a File Name for the export. | Files either exported from, or imported into the system. | Text in Bold Italic |
Variable and parameter names | Enter a Name for the export. | Variable and parameter names (not values). | Text in Italic |
Variable and parameter values | Enter a VALUE for the export. | Variable and parameter values. | Text in BOLD CAPS |
System output | Client.Domain.Models.ExportImportConfiguration | Any text output by the system. | Text in Monospace |
External links | Links to external sites that have information connected to the document or subject content. These could include:
| Selectable text to external sites | |
Internal documentation links |
If available, these links will be presented below the text. | Selectable text to internal content |
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
This product offers the possibility to process personal identifiable information such as system user name, role and IP-address. The purpose of this processing capability could be to enhance quality control through traceability and proper access management.
If you decide to process personal data you need to be aware of and comply with relevant personal data protection rules, including, in the EU the GDPR as well as other applicable laws, directives and regulations. Atlas Copco can in no way be held liable for any use made by you of the product.
Liabilities and Warnings
Liability
Many events in the operating environment may affect the tightening process and shall require a validation of results. In compliance with applicable standards and/or regulations, we hereby require you to check the installed torque and rotational direction after any event that can influence the tightening result. Examples of such events include but are not limited to:
initial installation of the tooling system
change of part batch, bolt, screw batch, tool, software, configuration or environment
change of air- or electrical connections
change in line ergonomics, process, quality procedures or practices
changing of operator
any other change that influences the result of the tightening process
The check should:
Ensure that the joint conditions have not changed due to events of influence.
Be done after initial installation, maintenance or repair of the equipment.
Occur at least once per shift or at another suitable frequency.
Warnings
About the User Guide
The User Guide describes how to set up and configure the PFHC.
It is intended for anyone operating or servicing the PFHC.
Revision History
Release Number | Revision Date | Revision Description |
|---|---|---|
item | item | none |
3.10 | 06/2023 | NEW content: |
3.9 | 01/2023 | NEW content:
UPDATED content:
|
3.8 | 09/2022 | First official release of the User Guide for Power Focus HC. |
Prerequisites
Anyone interested in learning more about PFHC can benefit from reading this User Guide.
For a complete understanding of the technical aspects described in the User Guide, we recommend the following:
Knowledge about tightening techniques
Experience of working with the previous versions of Power Focus
System Overview
Software Structure
Menu Overview
Web GUI which is accessed on the external computer, has several menus available to perform the following:
Configure tensioning and hardware accessories
Perform tool maintenance
Manage software
View reports
Controller GUI, shown on the hand controller's display, is a user interface for operation and monitoring of the system.
Web GUI
Tensioning Tab

The Tensioning tab lists the Tensioning programs stored on the hand controller that are available for an individual tensioning.
Tensioning configurations are described in the Tensioning tab.
Configuration Tab

A list of configurations is given in the Configurations tab. Common configurations are independent of the type of the connected tensioner and hydraulic pump.
Tensioner Controller Tab
The Controller tab lists hardware and software components.
The software versions stored and used in the hand controller are listed and can be updated.
It is also possible to import or export settings to and from the hand controller.
Reports Tab

The Reports tab lists the tensioning results and events.
Settings Tab
The Settings tab is used to set up the hand controller's specific settings, such as date and time, pin code, events, and wireless network.
Help Tab

The Help tab contains useful help sections about the hand controller.
Controller GUI
Tasks Tab

The Tasks tab lists the tensioning programs stored on the hand controller that are available for an individual tensioning. Tensioning configurations are described in the Tensioning tab in Web GUI.
Reports Tab

In the Reports tab, the tensioning results are listed and the report can be generated and saved on a USB flash drive.
Controller Information Tab

The Controller Information tab lists hand controller unit data such as serial number, IP address and software version.
Settings Tab

The Settings tab allows to set date and time and clear results.
Connected Devices Tab

The Connected Devices tab shows the connection status of the tensioner and pump that are connected to the hand controller.
It lists unit data of the connected tensioner and pump, such as serial number and software version. It also shows the current tensioner puller bar count.
Batch Sequence Tab

The Batch Sequence tab lists the batch sequences stored in the controller.
A Batch Sequence is one or more repetitive tightening programs in various combinations. Batch sequences are created and configured in the Batch sequence tab.
Operating and Handling
Web GUI
GUI Buttons and Icons
Button | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
Add | Add an additional item. | |
Remove | Remove an item. | |
| Ellipsis | Edit an item. |
Go back | Return to previous view. | |
Scroll up Scroll down | Move in a list that is too long for the screen. | |
Maximize Minimize | Maximize or minimize a section with parameters. | |
Back (to the start) (in a list) Back (in a list) | Move back in pages of a list. | |
Forward (to the end) (in a list) Forward (in a list) | Move forward in pages of a list. | |
Close | Tap to close the window. | |
Notice | Sign showing that a parameter is configured wrong. | |
WARNING | Sign leading to a warning about the risk of injury. | |
Validate program | Tap to check if a program is valid. | |
Download manual | Tap to download a manual. | |
Go home | Go to the Home screen. | |
Go result | Go to the live results screen. |
Controller GUI
GUI Buttons and Icons
Buttons on the hand controller keypad are context sensitive. Active buttons are represented by icons on the controller GUI. These icons show the current functionality of the keypad buttons. For example, on the Home view, active buttons are represented by the following icons, see the picture below:
Previous (left)
Next (right)
Up
Down
Enter
To navigate, use the left, right, up and down buttons on the keypad. To enter a menu or confirm a choice, use the Enter button in the middle.
For information about all icons on the controller GUI, see the table below.
1 | Previous |
2 | Next |
3 | Up |
4 | Down |
5 | Enter (select) |
6 | Wi-Fi and ToolsNet connection status |
Button | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | Back | Return to previous view |
 | Forward | Continue. |
 | Up Down | Move up or down in a list. |
 | Enter | Confirms the selected choice. |
  | More | Additional information or actions. |
 | Next | Go to the next view. |
 | Previous | Go to the previous view. |
 | Wi-Fi connection status | Connected to Wi-Fi |
 | Wi-Fi connection status | Not connected to Wi-Fi |
 | ToolsNet connection status | Connected to ToolsNet |
 | ToolsNet connection status | Not connected to ToolsNet |
LED Status Indicator
The LED matrix on the tensioner is mimicked on the hand controller GUI during the tensioning process. For more information about LED Status Indicator, see Product Instructions STT Tensioner.
Quick Start Guide
To create a better overview of the system, this section provides a quick guide covering the basic steps required to get started with the Smart Tensioning System and Power Focus Software.
The section does not explain every feature of the system, but instead focuses on the most basic ones.
To start the system, the pump and the tensioner must be connected to the hand controller before turning on power on the hydraulic pump with the power switch.
Rundown the tensioner straight on top of the bolt. Make sure that the socket inside the tensioner is engaged on the nut by moving the click wrench. Listen for the click sound. Observe that the tensioner rotates as the wrench applies some force on the nut.
When the Tasks icon on the hand controller is active, run Manual mode by using the keypad buttons on the hand controller.
Set the target pressure to a low pressure, for example, 500 bars, and then press the pressurize button.
If the motor is running, but there is no pressure increase, the most common problem is that the motor runs backwards. Power off the system and reverse the phases of the power connector, then try again.
When the system is pressurized, move the click wrench to see the Angle and Torque readings update.
For more detailed information about system startup of the Smart Tensioning System, see Smart Tensioning System Working Guide.
Installation and Upgrade
In this section, you can find information to help with the initial installation of the product, or upgrading from one version to another.
Web Browser Requirements
For optimal performance, use a web browser that has good JavaScript performance, and enable browser caching.
It is possible to run the software through the following web browsers:
Google Chrome 70 or later
Microsoft Edge 79 or later
Firefox 63 or later
Configuration
In this section, you can find detailed information about how to create, modify, and verify product settings.
Connecting to PFHC Configuration GUI
For optimal performance, use a web browser that has good JavaScript performance and enables browser caching.
Open the cover of the hand controller's USB connection port.
Connect a PC to the USB-C connector on the hand controller. To make sure that the PC gives enough power to the hand controller, use USB-3.0 ports.
To enter the configuration GUI, enter the following address in your browser: http://169.254.1.1/config.html.
See more information in the section Web Browser Requirements.
Web GUI
Live results
Open the live result screen by clicking the Results icon in the lower left corner when it is visible.
Status, torque and angle are displayed.
Click on the Connection icon in the upper right corner in the live result screen to open the Protocol status screen.
Viewing Protocol Status
On the Home view, select the Results icon and go to the Live Results view.
At the upper-right corner, select the
 button. The Protocol status dialog box appears.
button. The Protocol status dialog box appears.The tabs in the dialog box show the following information:
Tab
Description
Server Connections
Shows the status of the connections to ToolsTalk and ToolsNet servers: Enabled / Disabled

To change the configuration setting Enabled / Disabled, go to Settings > Server Connections and select the server to configure.
Launcher Status
Shows the launcher status of the different system adapters: OK / NOK
Select Close.
Working with the Tensioning Tab
This section describes the multistep tensioning strategy and how to create a tensioning program.
On the Home view, go to Tensioning tab, then select Multistep Program Library.
Multistep Configuration User Interface
The user interface for configuring a multistep program consist of the following main areas:
In the left pane under the Properties tab, there is a General Settings of the multistep tensioning program containing Program name.
In the left pane, the Program tab has a drop-down menu containing Steps.
To build the multistep program, click on Steps, then drag the appropriate step icon - Tensioning or Tensioning Service from the list to the tensioning area. Drop the selected step icon between the beginning and the end of the program.
The Tensioning Manual program is created automatically by the hand controller and can be edited as needed.
The main area of the user interface is made up of the tensioning area. This is the area that includes all the steps in the tensioning program.
Default Manual Program
In the Multistep Program Library, select Default Manual Program. The Default Manual Program is automatically created. The manual program can be run with all sizes and types of tensioner tools.
The manual program contains three settings for controlling the behavior of the manual mode. The name of the manual program can be edited in General Settings > Properties.
General Settings
General Settings consists of the field Name.
Select a program, go to Properties tab to edit General Settings by entering the name in the free text string field.
The chosen program name is displayed in the controller GUI in the listed programs under different job types in the Tasks tab.
Manual Mode Parameters
In the Default Manual Program, click on the Tensioning Manual icon in the tensioning area to edit the following parameters:
Name
Default manual hydraulic pressure (bar)
Max system hydraulic pressure (bar)
Parameter | Default | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
Name | Manual Mode Step | String name of the step | Not used since the manual mode does not generate any results. |
Default manual hydraulic pressure (bar) | 1000 | Used to populate the manual mode set pressure window when the manual mode runs for the first time after a system start. | The default manual pressure makes sure that the operator does not just reuse a previous pressure from an earlier manual mode run. Set the default pressure to a value applicable to your application. Once the manual mode has been used, the system will assume that this is the pressure that suits the ongoing operation. The last used pressure will be used as the manual mode pressure until the system is powered off. It is always possible to change the target pressure in the controller GUI. |
Max system hydraulic pressure | 1980 | The highest pressure target that is allowed when using this configuration. | The system is using the lowest max pressure of its connected units. If any of the connected units have a lower max pressure, the pressurization will stop at this pressure level. |
Tensioning Program
On the Home view, select the Tensioning Tab. Multistep Program Library is selected automatically.
To add a tensioning program, click on the Plus icon above the program list to open the Program tab, then click on Steps.
If any tensioning program is already available, select the program to edit it.
Drag and drop the tensioning steps in the tensioning area.
Steps can only be placed between the start and the end point of the program.
Buttons Delete Tightening Program and Copy Tightening Program are available at the lower-right corner for deleting and copying the program.
A tensioning system uses only one step per configuration.
Changes made to tightening programs in any section need to be actively applied by clicking the Apply button in the bottom right corner of the GUI. Alternatively, changes can be undone by clicking the Undo button in the same location.
When navigating away from the section where changes have been made (by using the Back, Home or Result button), the user will be presented with a warning pop-up where the changes can also be applied or undone. The user cannot proceed without applying or undoing changes.
Function | Description | |
|---|---|---|
Start and end points |  | Start and end points of the Multistep program. All steps must be placed between these two points. |
Showing step properties |  | Click on the step to reveal the properties. |
Closing step properties |  | Click anywhere in the tightening area to close the properties menu. |
Deleting a step |  | Click on the step properties and then Delete at the bottom of the menu. |
Step error |  | When a validation error occurs in a step, that step will be marked. Note that when the step properties are opened, the parameter causing the error will also be marked. Click on the red mark for more information about the error. |
Forbidden placement |  | When a particular placement of a step is not allowed, the placeholder icon will not be shown. |
Tensioning Parameters
Under Program tab, click on the Tensioning item to open it and edit the parameters. The tensioning parameters are listed in the table below. See also Diagram of the tensioning process in the section Tensioning process.
Parameter | Default value | Unit | Description | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a All default values are tailored for an M36 bolt running with min angle 40 degrees and no max angle. b The rotation detection parameters define an expected play in the wrench-socket-gear box chain. The experience is that this can vary a lot depending on, mainly bolt geometry – even when the tool is attached to the same bolt but the socket aligns to different sides of the nut. c The rotation detection parameters define an expected play in the wrench-socket-gear box chain. The experience is that this can vary a lot depending on, mainly bolt geometry – even when the tool is attached to the same bolt but the socket aligns to different sides of the nut. | |||||
Name |
| User name of the step configuration, written in the xml report file and reported in the step Results. | |||
Bolt size | M36 a | mm | The size of the bolt for the intended configuration. The bolt size is compared to the connected tool and if it does not match, an invalid configuration event is emitted. | The controller GUI filters out the configurations that fit the connected tools. Configurations made for other tool sizes are not displayed in the list under Tasks > Assembly or Tasks > Batch Assembly. | |
Tensioner type | Flange bolt | Tensioner type must match the connected tensioner. The string is compared to the string that identifies the type of tensioner which is programmed in the tensioner during its production. The string is case sensitive when compared to the string in the tensioner. | The controller GUI filters out the configurations that fit the connected tools. Configurations made for other tensioner types are not displayed in the list under Tasks > Assembly or Tasks > Batch Assembly. | ||
Min nut rotation angle | 40 | Degrees | The minimum nut rotation angle for an OK tensioning. | The field can be left empty if the tensioning process does not depend on minimum tightening angle. | |
Max nut rotation angle | Degrees | The maximum nut rotation angle for an OK tensioning. | The field can be left empty if the tensioning process does not depend on the maximum tightening angle. | ||
Angle approval | Approve last angle | Controls the behavior of the angle measurement when re-tensioning after NOK result. Choices are:
| For configurations that require max angle, it is recommended to use only the last angle. For configurations that require min angle, use angle summarization in order to consider the sum of all attempts for OK/NOK results. For configurations that define an angle range, consider which behavior applies for the job the that the configuration is tailored for. | ||
Use clamping force estimation | On | Controls which clamping force estimation is used for the result. On -> Clamping force estimation is used: tensioning force – Estimated Initial mean settlement Off -> clamping force is calculated according to Load Transfer Factor equation: tensioning force / (1.01 + (bolt diameter / clamping length)) | The Atlas Copco (AC) Load Transfer Factor (LTF) equation utilized in the STS is for use on ‘Flange’ connected joints only. Do NOT use on foundation style joints. | ||
Clamping length | mm | The height of the flange, i.e. the distance between the nuts on each side of the flange. Active when: Use clamping force estimation is ’Off’. | Visible if Use clamping force estimation is ’Off’. | ||
Estimated initial mean settlement | 99 | kN | An estimation of the average force loss when releasing the pressure. Active when: Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. | Visible if Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. It is used in the xml report generation. The value depends on the tensioner size and the type of the flange. | |
Estimated initial max settlement | 155 | kN | An estimation of the maximum force loss when releasing the pressure. Active when: Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. | Visible if Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. It is used in the xml report generation. The value depends on the tensioner size and the type of the flange. | |
Min required average clamping force | 510 | kN | The minimum average clamping force for all bolts on the flange used in flange summary section in the xml report. Active when: Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. | Visible if Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. It is used in the xml report generation. The value depends on the tensioner size and the type of the flange. | |
Batch job report type | General | Controls the flange summary generation in the xml reports:
| Tailored for customer-specific xml report requirements: First round, Second round, User General for Service jobs. | ||
Angle sensor reset force | 100 | kN | The force at which the angle measurement reference for 0 degrees is set. | The expected angles are calculated depending on the force increase from the angle sensor reset force to Min bolt tensioning pressure. This evaluates to different pressures depending on the tensioner size, see the table in the section Pressures for Different Tensioner Sizes. The larger the tensioner is, the higher the angle reset force must be set, due to issues with control of low pressures in installation check step. This is necessary in order to avoid overshooting of Installation check hydraulic pressure higher than pressure equivalent of angle sensor reset force. | |
Min bolt tensioning pressure | 1900 | Bar | The min pressure for an OK tensioning result. | The pressure control in the system will set a target value higher than the Min bolt tensioning pressure to avoid pressure drop ending in a NOK result. See the picture in the section Hydraulic Pressure Target Window. | |
Max system hydraulic pressure | 1980 | Bar | The highest pressure the pressure control in the hand controller allows for this configuration. | The actual max pressure is the lowest of the max pressures in the pump and tensioner and the Max system hydraulic pressure of the configuration. | |
Min bolt tensioning force | 698 | kN | Force equivalent of the Min bolt tensioning pressure parameter. | Value manually calculated from bolt pressure. This value is written in the xml report files, but it is not used by the hand controller's software. | |
Installation check torque | 20 | Nm | The required torque for an acknowledged installation check. | ||
Installation check torque duration | 1.0 | S | The required time the Installation check torque must be applied for an acknowledged installation check. | ||
Tightening target torque | 100 | Nm | The required torque for an acknowledged tightening of the nut. | ||
Tightening torque duration | 1.0 | S | The required time the Tightening target torque must be applied for an acknowledged tightening of the nut. | ||
Tightening unexpected clockwise rotation detection angle | 5 | Degrees | The maximum allowed change of the nut rotation angle in clockwise direction when the process is waiting for pressure release. | To avoid the risk of nut rotation while the system waits for pressure release, activate automatic pressure release (see section Tool Configuration). b | |
Tightening unexpected counter clockwise rotation detection angle | 5 | Degrees | The maximum allowed change of the nut rotation angle in counter clockwise direction when the process is waiting for pressure release. | To avoid the risk of nut rotation while the system waits for pressure release, activate automatic pressure release (see section Tool Configuration). c | |
Installation check hydraulic pressure | 20 | Bar | The pressure set point for installation check. | The installation check pressure fixes the tensioner to the flange during the installation check. The installation check pressure, including overshoot, must not exceed the pressure equivalent of Angle reset force. | |
Hydraulic pressure set point factor | 1.025 | The actual set point for the pressure regulation is calculated as follows: Min bolt tensioning pressure times Hydraulic pressure set point factor. See the picture in the section Hydraulic Pressure Target Window. | When pressing and holding the pressurization button, the system is pressurized, the pressure will be held inside a pressure window above Min bolt tensioning pressure. | ||
Tensioning Process
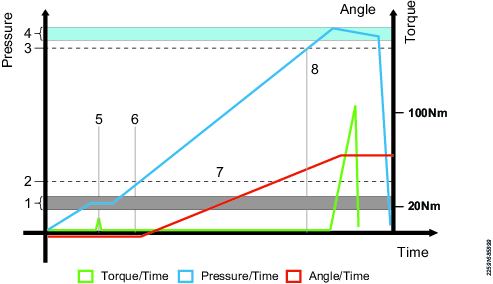
1 | Installation check hydraulic pressure |
2 | Angle reset force |
3 | Min bolt tensioning pressure |
4 | Pressure target window. With the pressurize button held, the system will keep the pressure within this window |
5 | Installation check. Sets mechanics in a known position. The nut does not rotate. The play in ratchet and gearbox is fixed in the tightening direction. |
6 | The angle reference point is sampled. Tightening angle measurement starts from this point. |
7 | Pressure builds up, rotation of the nut OK but no need to apply any high torque. Let the hydraulics do the work. |
8 | Min bolt pressure reached. Final fixation of the nut. |
If the installation check pressure ends higher than the pressure that corresponds to angle reset force, the tensioning process cannot set its angle reference point (6).
Therefore, the parameter angle reset force may have to be adjusted, depending on tensioner size, to include some margin for installation check pressure overshoots. The actual installation check pressure depends on, for example, oil type or oil temperature. See the table in section Pressures for Different Tensioner Sizes.
Pressures for Different Tensioner Sizes
Angle reset force 100kN with calculated equivalent pressures for different tensioner sizes are shown in the Table 1.
Tensioner | Angle reset force (kN) | Angle reset pressure (in bar) |
|---|---|---|
M36 | 100 | 272 |
M42 | 100 | 198 |
M48 | 100 | 151 |
M56 | 100 | 109 |
M64 | 100 | 83 |
M72 | 100 | 64 |
Angle reset force settings for different tensioners with margin for installation check pressure are shown in the Table 2.
Tensioner | Angle reset force (kN) | Angle reset pressure (in bar) |
|---|---|---|
M36 | 100 | 272 |
M42 | 100 | 198 |
M48 | 150 | 226 |
M56 | 200 | 219 |
M64 | 200 | 166 |
M72 | 250 | 161 |
Hydraulic Pressure Target Window
The picture below illustrates how the system keeps the pressure inside the pressure target window while holding the pressurize button pressed.
See also the Diagram of the tensioning process in the section Tensioning Process.
1 | Min bolt tensioning pressure (y) |
2 | Hydraulic pressure target (x) |
3 | Hydraulic pressure hysteresis level (x-y)/3 |
Calculation
Hydraulic pressure target (x) = Min bolt tensioning pressure (y) × Hydraulic pressure target factor (k)
Hydraulic pressure hysteresis level = 1/3 of the distance between Hydraulic pressure target (x) and Min bolt tensioning pressure (y).
The pressurization starts at this level to keep it above the minimum level.
Bolt Service Parameters
Parameter | Default value | Unit | Description | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
a All default values are tailored for an M36 bolt running with min angle 40 degrees and no max angle. b The rotation detection parameters define an expected play in the wrench-socket-gear box chain. The experience is that this can vary a lot depending on, mainly bolt geometry – even when the tool is attached to the same bolt but the socket aligns to different sides of the nut. c The rotation detection parameters define an expected play in the wrench-socket-gear box chain. The experience is that this can vary a lot depending on, mainly bolt geometry – even when the tool is attached to the same bolt but the socket aligns to different sides of the nut. | |||||
|
Name | User name of the step configuration, written in the xml report file and reported in the step Results. | ||||
Bolt size | M36 a | mm | The size of the bolt for the configuration intended for it. The bolt size is compared to the connected tool and if it does not match, an invalid configuration event is emitted. | The controller GUI filters out the configurations that fit the connected tools. Configurations made for other tool sizes are not displayed in the list under Tasks > Bolt Service or Tasks > Batch Bolt Service. | |
Tensioner type | Flange bolt | Tensioner type must match the connected tensioner. The string is compared to the string that identifies the type of tensioner which is programmed in the tensioner during its production. The string is case sensitive when compared to the string in the tensioner. | The controller GUI filters out the configurations that fit the connected tools. Configurations made for other tensioner types are not displayed in the list under Tasks > Bolt Service or Tasks > Batch Bolt Service. | ||
Max delta nut rotation | 13 | Degrees | The max total allowed rotation of the nut for the bolt service process, i.e. the maximum nut rotation in tightening direction compared to the starting point. | See also section Bolt Service Process. | |
Min delta nut rotation | 0 | Degrees | The minimum actual nut rotation that is allowed for the bolt service process. | Min delta nut rotation and max delta nut rotation create a range of accepted result of the bolt process, e.g. 0.13 - the nut needs to return to its original position (Min delta nut rotation = 0) but must not rotate more than 13 degrees in the tightening direction Max delta nut rotation = 13). A value < 0 for Min delta nut rotation allows that the nut does not return completely to the original position. | |
Use clamping force estimation | On | Controls which clamping force estimation is used for the result. On -> Clamping force estimation is used: tensioning force – Estimated Initial mean settlement Off -> clamping force is calculated according to Load Transfer Factor equation: tensioning force / (1.01 + (bolt diameter / clamping length)) | The Atlas Copco (AC) Load Transfer Factor (LTF) equation utilized in the STS is for use on ‘Flange’ connected joints only. Do NOT use on foundation style joints. | ||
Clamping length | mm | The height of the flange, i.e. the distance between the nuts on each side of the flange. | |||
Estimated initial mean settlement | 99 | kN | An estimation of the mean force loss when releasing the pressure. Active when: Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. | Visible if Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. It is used in the xml report generation. The value depends on the tensioner size and the type of the flange. | |
Estimated initial max settlement | 155 | kN | An estimation of the maximum force loss when releasing the pressure. Active when: Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. | Visible if Use clamping force estimation is ’On’. It is used in the xml report generation. The value depends on the tensioner size and the type of the flange. | |
Min required average clamping force | 510 | kN | The minimum average clamping force for all bolts on the flange used in flange summary section in the xml report. | It is used in the xml report generation. The value depends on the tensioner size and the type of the flange. | |
Batch job report type | General | Controls the flange summary generation in the xml reports:
| |||
Nut loosening attempt count torque | 75 | Nm | The torque limit for a loosening attempt. If the number of attempts passes Nut loosening number of attempts, the bolt service process prompts the user to tighten the bolt again because it was not possible to loosen it. | ||
Nut loosening number of attempts | 3 | The number of attempts with torque higher than Nut loosening attempt count torque before prompting the user to tighten the nut again since it was not possible to loosen it. | |||
Nut loosening min loosening angle | 10 | Degrees | The required loosening angle for an acknowledged bolt service operation. | ||
Angle sensor reset force | 100 | kN | The force at which the angle measurement reference for 0 degrees is set. | The expected angles are calculated depending on the force increase from the angle sensor reset force to Min bolt tensioning pressure. This evaluates to different pressures depending on the tensioner size, see the table in the section Pressures for Different Tensioner Sizes. The larger the tensioner is, the higher the angle reset force must be set, due to issues with control of low pressures in installation check step. This is necessary in order to avoid overshooting of Installation check hydraulic pressure higher than pressure equivalent of angle sensor reset force. | |
Min bolt tensioning pressure | 1900 | Bar | The min pressure for an OK tensioning result. | The pressure control in the system will set a target higher than the Min bolt tensioning pressure to avoid pressure drop ending in a NOK result. See picture in the chapter Hydraulic Pressure Target Window. | |
Max system hydraulic pressure | 1980 | Bar | The highest pressure the pressure control in the hand controller allows for this configuration. | The actual max pressure is the lowest of the max pressures in the pump and tensioner and the Max system hydraulic pressure of the configuration. | |
Min bolt tensioning force | 698 | kN | Force equivalent of the Min bolt tensioning pressure parameter. | Value manually calculated from bolt pressure. This value is written in the xml report files, but it is not used by the hand controller's software. | |
Installation check torque | 20 | Nm | The required torque for an acknowledged installation check. | ||
Installation check torque duration | 1.0 | S | The required time the Installation check torque that must be applied for an acknowledged installation check. | ||
Tightening target torque | 100 | Nm | The required torque for an acknowledged tightening of the nut. | ||
Tightening torque duration | 1.0 | S | The required torque for an acknowledged tightening of the nut. | ||
Tightening unexpected clockwise rotation detection angle | 5 | Degrees | The maximum allowed change of the nut rotation angle in clockwise direction when the process is waiting for pressure release. | To avoid the risk of nut rotation while the system waits for pressure release, activate automatic pressure release (see section Tool Configuration). b | |
Tightening unexpected counter clockwise rotation detection angle | 5 | Degrees | The maximum allowed change of the nut rotation angle in counter clockwise direction when the process is waiting for pressure release. | To avoid the risk of nut rotation while the system waits for pressure release, activate automatic pressure release (see section Tool Configuration). c | |
Installation check hydraulic pressure | 20 | Bar | The pressure set point for installation check. | The installation check pressure fixes the tensioner to the flange during the installation check. The installation check pressure, including overshoot, must not exceed the pressure equivalent of Angle sensor reset force. | |
Hydraulic pressure set point factor | 1.025 | 1.025 | The actual set point for the pressure regulation is calculated as follows: Min bolt tensioning pressure timesHydraulic pressure set point factor. See the picture in the section Hydraulic Pressure Target Window. | When pressing and holding the pressurization button, the system is pressurized, the pressure will be held inside a pressure window above Min bolt tensioning pressure. | |
Bolt Service Process
To guarantee the results for loosening and tightening angle, follow the bolt service process:
Position the tool on the bolt.
Pressurize to Installation check hydraulic pressure.
Do an installation check for bolt service:
Apply torque >20 Nm in tightening direction. Hand controller takes angle reference point in tightening direction.
Apply torque >20 Nm in loosening direction. Hand controller takes angle reference point in loosening direction.
Hand controller stores the angle of the mechanical play.
While keeping the wrench and gearbox in loosening position, press and hold the pressurize button until the pressure reaches Min bolt tensioning pressure bar.
Loosen the nut to an angle greater than or equal to the bolt service parameter Nut loosening min loosening angle.
The controller UI will show the loosening angle as a negative measurement from the loosening angle reference point.
Tighten the bolt to the parameter Tightening target torque. The tightening angle is recorded.
Loosening and tightening angles refer to actual nut rotation. Hand controller compensates for mechanical play. The controller GUI will start updating the angle when the nut starts to rotate, i.e. disregarding the mechanical play. Thereby the displayed angle will reflect the nut movement, and when the angle measurement is 0, the nut is back to the original position.
The delta nut rotation in tightening direction must not be higher than parameter Max delta nut rotation with default of 13 degrees. In practice, this means that the nut must not rotate to an angle more than 13 degrees higher than the original position.
Release pressure and store result. The following conditions must be true to get OK results:
The recorded loosening angle is greater than or equal to Nut loosening min loosening angle.
The recorded delta angle after tightening must be in the range between Min delta nut rotation and Max delta nut rotation.
Min delta nut rotation is equal to D in the picture Bolt service process.
1 | Wrench transport to tightening alignment |
2 | Nut rotation starts here |
3 | Tightened to original position |
A | Loosening angle |
B | Fix point loosening |
C | Play |
D | Fix point tightening |
E | Allowed tightening range after loosening is between minimum and maximum delta nut rotation parameters |
F | Max nut rotation |
Working with the Sources Tab
Controller features, such as the Low Reaction Tightening Strategies and controller-wide functions among others, require licenses distributed through the Functionality Management System (FMS). Whereas configuration of features is possible without specific licenses, the assignment and use of those features will require the correct license to be installed on the controller. Please refer to Licenses (FMS) for more detailed information on licenses.
External signals used as tasks for tightenings are configured in the Sources menu. Sources are accessories or similar connected to a virtual station. Two types of source tasks are available:
Source Tightening task
Source Batch task
Source Tightening is used to select a single tightening program.
Source Batch is used to select a batch sequence, a series of tightening programs.
For more information about selection of tasks, see Assigning a Task to a Virtual Station.
Source Tightening
The tightening menu shows a list of source tightening configurations. Separate lists can be linked to a Virtual Station by going to the Virtual Station in question, and choosing Task, Change task. There, a Source can be chosen as a task. Source tightenings link a specific tightening program to an identifier number. When the identifier is sent to the controller via external open protocol client the linked program will run.
Source Tightening lists can be set either in Control or Confirm mode.
When set to Control (not supported for PFHC), an external source selects a tightening program by requesting an identifier number.
In Confirm mode, the program numbers are linked to a source tightening program.
Product Essentials Tutorials
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vVAaKtp3O5k
Creating a Source Tightening
Changes made to tightening programs in any section need to be actively applied by clicking the Apply button in the bottom right corner of the GUI. Alternatively, changes can be undone by clicking the Undo button in the same location.
When navigating away from the section where changes have been made (by using the Back, Home or Result button), the user will be presented with a warning pop-up where the changes can also be applied or undone. The user cannot proceed without applying or undoing changes.
Go to the Sources menu, then select Tightening on the left navigation.
Click the plus icon in the top right of the workspace.
Give the Source Tightening a name and select the correct Selector mode (Control or Confirm, depending on what is required).
By default, only one editable Identifier number will be available when creating a new Source Tightening. At the bottom of the screen, click the plus icon to add more.
Give every item an identifier number

If a socket selector is used, the identifier numbers will correspond to the positions in the socket selector, i.e. Identifier number 1 corresponds to socket number 1 in the socket selector.
Choose a tightening program to link to each identifier number by clicking on Program and choosing from the list of tightening programs.
Sources - max consecutive NOK
Max consecutive NOK can be set per Source Tightening or per individual program included in the Source Tightening.
Set Max consecutive NOK per program to No
Set the value in the Max consecutive NOK field.
Set Max consecutive NOK per program to Yes
For every program in the Identifier selector configuration section, set the value in the Max NOK column.
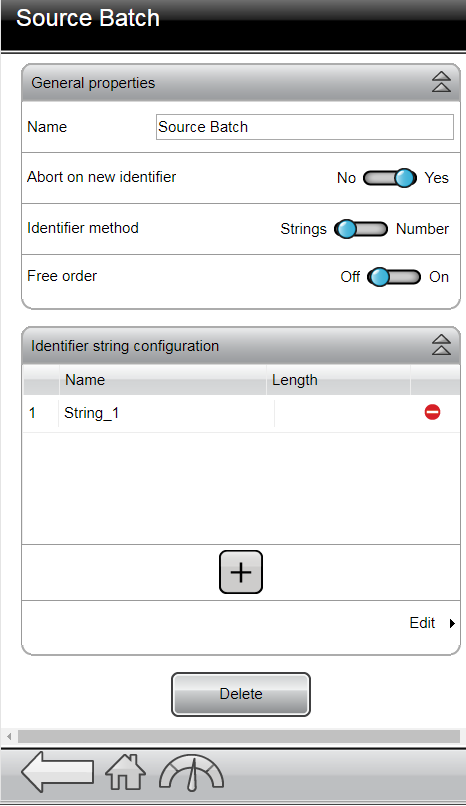
Source Batch Sequence
Source Batch is not yet fully supported in PFHC. Use with caution.
The Source Batch configuration is found under the Batch option in the Sources menu.
The controller can be configured to select a batch sequence based on either an identifier number or an identifier string.
Input | Description |
|---|---|
Identifier number | The number must be a positive integer number that can originate from an accessory or from an external control entity. |
Identifier string | The string must consist of ASCII characters and can originate from a scanner or from an external control entity. |
Socket selector | The use of one or several socket selectors. |
Product Essentials Tutorials
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-dTjDz6ravw
Creating a Source Batch
Go to the Sources menu, then select Batch sequence on the left navigation.
Click the plus icon in the top right of the workspace.
Give the Source Batch a name
Set the Abort on new identifier to Yes if scanning a new identifier string should abort the previous scan.
Select the Identifier method (String for text, or Number for numerical strings)
Set Free order to On if the strings should be able to be scanned in any order.

Identifier strings can be made up of up to 4 different strings. When free order is set to No, the strings need to be scanned in a specific order for the system to recognize the string.
If required, add an identifier string by clicking on the Plus icon in the Identifier string configuration section.
Click on the Name label for the identifier string you want to change the properties of (pop-up window). The following properties can be indicated per string:
Name - the name of the string
Length - the length of the string. See Combining Identifier Strings for more information on concatenating strings.
Significant positions - used to specify which characters in the barcode string to read when putting together the string to match with your pre-defined string. The number of significant positions must match the number of characters in the pre-defined strings.
Saved positions - indicate which parts of each string used in the Source Batch is saved, and how they are represented in the log. In this field, indicate the positions in the string that need to be saved. Positions can constitute only parts of the entire string. If the field is left empty, the entire (concatenated) string will be saved. The table below shows some examples of saved position combinations.
Saved position values are comma-separated (without spaces), and ranges are indicated using a hyphen.
Identifier string
Positions
String 1: 1234567
1-7
String 2: abcdef
8-13
String 3: GHIJKL
14-19
String 4: 890
20-22
Saved position examples Saved positions
Saved results
(empty)
1234567abcdefGHIJKL890
1-3,9,11,15,20-22
123bdH890
8-12,1-7,19,20-21 will be changed automatically to: 1-12,19-21
1234567abcdeL89

The ID field in the string properties window cannot be altered, but can only be used to navigate between the different strings.

An error may occur when Free order is set to On, and the lengths of the different strings are duplicated. The scanned sequence will then not activate a tightening program. To remedy this error, set Free order to Off, or adjust the string lengths.
Click Edit.
In the Edit window, indicate which strings (in the String contains column) should be linked to which Batch sequence (in the Activates column). Click the plus icon at the bottom to add more strings.

Wildcards can be used when typing the "string contains". The wildcard(s) can be used at any position in the string. No Batch sequence is activated in case of an ambiguous matching result.
The wildcard is a . (period)
Configuring Significant Positions to Read in Barcode String
The positions in the barcode string are associated with a number between 1 and 1024. The first position of the string is 1 and the last is 1024.
Description | Significant positions | Valid configuration | Barcode string to match with pre-defined string |
|---|---|---|---|
Significant positions in order | 1,2,3,7,8 | Ok | ABCGH |
Significant positions in optional order | 7,1,2,3,8 | Ok | GABCH |
Range of numbers | 1–3,7-8 | Ok | ABCGH |
Combining Identifier Strings
The identifier string that is used for matching is a combination of up to four strings from a factory management system or up to four scanner inputs that need to be combined into one string.
The Add and Delete command buttons manage how many strings are combined. The following parameters are available:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Check box | Select an entry if it is to be deleted. |
Name | The string must be given a name. |
Length | The length of the string must be known and must be entered. This is important to be able to combine the correct string identifier. |
Significant positions | The comma-separated positions or ranges (separated by hyphen) in the combined string that are used for matching. |
Saved positions | The comma-separated positions or ranges in the strings that will be saved in the result. |
If more than one identifier string is to be used, perform the following steps:
Press the Add command button to create a new entry in the table.
Issue the string a name.
Enter the length of the string.
Repeat steps 1-3 for every string to be added. Up to four strings can be combined.
The Start-End parameters in each row define the individual string positions in the combined string identifier that is used in the next step of the matching process.
The first part in the task selection process using an identifier string as an input, is to define which positions in the string that are to be activated:
Enter the significant positions, to define which positions in the identifier string will be used for matching. The positions must be either comma-separated, or by range.
Working with the Configurations Tab
Configurations of the tools are made in the Configurations menu.
Tool Configuration
On the Home view, go to the Configurations > Tool Configuration to configure the available functions in the system.
Enter a name in the Name field.
Edit a configuration by clicking on the Edit button. See the table below.
To create additional configuration with different settings, click on the plus icon at the top of the page.
For example, create a configuration with Automatic pressure release = ON, or Pump motor timeout with different time.To choose a configuration to use, go to the Home view, Tensioner Controller > Tool.
Parameter | Default value | Unit | Description | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Pump motor time-out | 30 | s | Timer for pump motor cooldown, also controlling the hydraulic oil return valve. The pump motor stops when the timer expires and the hydraulic return valve closes. When pressure is released, the hydraulic oil return valve is opened and the motor runs for 6 seconds. Then the pump motor time-out starts and when it expires, the valve is closed and the motor stops. | When the system is used in warm conditions, the hydraulic oil may overheat if the motor stops. For larger tensioners, the transport of hydraulic oil back to the pump oil container may need more than the minimum time of 6 seconds. |
Automatic pressure release | OFF | When the automatic pressure release is ON, the pressure is automatically released when the nut is tightened according to settings - the tensioning is completed. | The pressure is released when the torque is relaxed after being applied for the required torque and the required time. See the Diagram of the tensioning process in the section Tensioning Process. Recommended setting for this parameter is ON for the following reasons:
|
Working with the Tensioner Controller Tab
Virtual Station
A virtual station is a software abstraction of a hand controller. The hand controller has an integrated controller with one connected virtual station. Various configurations can be assigned to the virtual station as needed.
Working with the Virtual Station Tab
Virtual stations are configured in the Virtual Station menu.
A virtual station is a software abstraction of a physical station and can be set up to use a specific tool and remotely execute different tasks using the tool.
In PFHC, it is possible to set up a number of virtual stations per controller. Each virtual station can be connected to one tool and one or more accessories.
By using virtual stations, the operator can operate multiple tools and run different tasks using the same controller. It is possible to connect one cable tool and multiple STB tools simultaneously to the controller.
When configuring different tools, make sure the selected start signal in Start source matches the selected tool and that the selected task can be run on the specific tool.
Before any tightening can begin a task must be selected in the virtual stations menu. A task is of one of three types:
Tightening program
Batch sequence
Sources
The selection can be made manually by the operator or by external signals.
Product Essentials Tutorials
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ay0zO5fGSD8
Configuring Task Window in a Virtual Station
The selected task can either be running a tightening program, running a batch sequence or enabling the task using a source configured in the Sources menu.
The task can be monitored from the controller and the result of the task can be presented together with any events that may have occurred during the operation.
Configuring Protocols Window in a Virtual Station
Under the tab Protocols, in the Virtual Station menu, you will find a list of available communication protocols depending on the current license in use. The Open Protocol is available for all licenses.
To gain access to functionality through Open Protocol, a unique port for each Virtual Station needs to be defined.
Set the Open Protocol switch to On.
Enter the Server port number.
Enter the Communication timeout value in seconds, between 15 and 60.
Choose the action to be applied when the connection to the client is lost.
The Disconnect setting controls the action applied when a connection error occurs:
None - The tightening program continues normally.
Lock tool - The tool is locked after finishing the current tightening normally.
Unassign task - The tightening is ended after finishing the ongoing task. Except for plain tightening programs or Batch sequences where the task will be removed after finishing.
Always lock tool - The tool is locked after finishing the current tightening, regardless of result.
Use legacy counter
The legacy counter setting counts all tightenings in a sequence and outputs that number to secondary systems. To enable this setting, set Use legacy counter to Yes.
MID0015 Echo selected identifier number
This setting allows for responding the selected identifier number value in MID0015 PSET_SELECTED if MID0015 Echo selected identifier number set to Yes. Otherwise, the actual tightening program id is sent.
Tap or select Apply when ready.
Tool
Tool information shows data from the tensioner.
Model: socket size and tensioner type. A compatible configuration must have the fields Bolt size and Tensioner Type identical to the string (case sensitive) under Model to be compatible with the connected tensioner. If a configuration is not displayed under HCGUI -> Tasks -> Assembly bolt service the reason is likely to be identified in these two properties.
Gear ratio: the ratio of the gear box in the tensioner.
Serial number: the serial number of the tensioner.
Max torque: the highest torque that does not damage the torque sensor.
Software version.
Product number: the article number of the tensioner.
Intelligent Application Module
The Intelligent Application Module (IAM) is a non-volatile storage that is located in the hand controller. The storage module contains all the tool programs, configurations and results.
Go to Tensioner Controller tab in the home menu and select IAM.
Apply a string field Name to the hand controller.
The Name will be used in the Web GUI and on the hand controller GUI.
Software Versions
Two software versions can be installed in the tool simultaneously. Installing a second version of the software can be useful as preparation when upgrading multiple hand controllers for synchronized activation.
Changing software versions does not transfer the tool configurations or tensioning programs.
Software Activation
The hand controller can store two installed software versions. By using the Software activation, it is possible to choose which software version to use.
Go to Tensioner Controller in the home menu and select Software in the left pane.
Select Current or Stored in the Software Activation window.
The hand controller is automatically restarted for the activation to take effect.
Update Software Version
If the software package to be installed is not compatible with the hand controller's hardware, the software update will be cancelled. A warning message will be shown, pointing out which parts of the hardware that caused the cancellation.
For information on the current tool hardware, go to Tensioner Controller > Hardware.
Go to the Tensioner Controller menu and select Software in the left pane.
Go to the Software Update field and select BROWSE.
Browse and choose the zip file with the applicable software and follow the instructions to finish installation.
Hardware
The Hardware tab contains Controller information, such as model designation and serial number.
It is possible to do a warm restart of the hand controller in the window Restart Controller. Click on the RESTART button.
Exporting and Importing Configurations
The export and import functions are used to export events and tensioning results for analysis in external programs, as well as allowing for transferring of tensioning programs and tool configurations between tools.
The export function is used to:
Export tensioning results and events for further processing.
Export log files for debug assistance from an Atlas Copco service engineer.
Export tool configuration that can be used to copy settings to another tool.
Go to Tensioner Controller in the home menu. Select Export/Import in the left pane.
Select what to export from the tool:
All information
Settings and configurations
System logs and information
Results

When exporting parameters to be imported in other controllers, choose Settings and configurations.
When Settings and configurations is chosen, no file with results or events will be exported into the archive. With this setting the export takes less time to do.
Select EXPORT. A prompt to select where to save or retrieve the exported file is shown.
Go to Tensioner Controller in the home menu. Select Export/Import in the left pane.
Select IMPORT. When using the import function, all settings for tensioning programs and configurations are replaced by the settings from the import file. However, settings for network, PIN, and results and events are not imported.
Select CONTINUE in the dialog box to start the import.
Exported Information and File Format
The exported file is a compressed file archive containing the following files:
All information
PFExport_<datetime>_Results.csv
PFExport_<datetime>_Events.csv
ExportInfo.txt
settings/settings.zip
atlas_tool_i.zip
atlas_sys_i.zip
atlas_subsystems_info.zip
atlas_plc.zip
jsonConfigurations.zip
Settings and configurations
ExportInfo.txt
settings/settings.zip
jsonConfigurations.zip
File | Description |
|---|---|
PFExport__<Tool name>_<Time stamp>_Events.csv | A semicolon-separated file containing the following information:
|
PFExport__<Tool name>_<Time stamp>_Results.csv | A semicolon-separated file containing the following information:
|
ExportInfo.txt | Information about the tool set-up and tool software. |
settings/settings.zip | A binary file containing all tightening programs and Batch settings, Accessory configurations, and tool settings such as: Language, Torque units, Date and time, and Result appearance. |
atlas_tool_i.zip | Tool logs (for debugging) |
atlas_sys_i.zip | Logfiles from IT application |
atlas_subsystems_info.zip | Info about subsystem software |
atlas_plc.zip | PLC configuration |
jsonConfigurations.zip | Multistep Tightening and Loosening programs |
Exporting "System Logs and Information"
With this export a service technician can share the system logs and its information with Atlas Copco Service technicians, in order to facilitate troubleshooting.
The export of system logs and information does not include logs from the connected tool(s).
All data included in the export of system logs and information are stored in a file PFExport_<IAM name>_<datetime>.tar.gz, which includes the following files and directories:
atlas_sys_i.zip - Log files from IT application
atlas_protocol_log.zip – Log files from external protocol adapters
ExportInfo.txt - Text document containing information about the IAM and controller
licenseInformation.zip – License information and system capabilities
atlas_systeminformation.zip – Information to Atlas Copco R&D for current system health and setup
How to Export "System Logs and Information"
Go to Tensioner Controller in the home menu and select Export/Import in the left pane.
In the Export window, open the drop-down menu and select System logs and information.
In the Export window, select EXPORT.
At the end of the exporting process, an exporting pop-up window confirms that the export is done.
A PFExport_<IAM name>_<datetime>.tar.gz file is automatically downloaded.
Working with the Reports Tab
Viewing Results
This section describes how to access tensioning results from the hand controller, and how to read the information given in the different result views.
When a tensioning is performed, the result is stored in the hand controller. Results can also be sent to an external system such as ToolsNet, or exported for analysis using the export function. For more information about statistical analysis, result filtering and tensioning analysis using ToolsNet, refer to the ToolsNet 8 User Guide.
Stored Results
Each task is displayed as one result. A single tensioning can show results in a table with key parameters.
Stored Results View
The hand controller stores the result for every tightening or loosening performed.
Go to Reports in the home menu and select Results in the left pane.
Select View all results. The result list will show information about the following:
Date: date and time the tensioning was performed.
Tightening Program: Tightening Program column shows Multistep Tensioning Program name.
Force: measured force during tensioning.
Pressure: measured pressure during tensioning.
Result: Torque / Angle result.
Limits: Torque range, angle range and pressure range for an OK result. In NOK results the violated range limit is highlighted with red text.
Results marked with a red bar have status NOK.
Viewing Events
Events are used to notify the user of certain state changes or occurrences in the system. They are divided into three types; Information, Warnings and Errors and require different kinds of actions.
Each event has a default setting for whether it should be acknowledged (Ack), logged (Log) or displayed (Disp). These settings can be configured in the Settings menu under Events.
Go to Reports in the home menu and select Events in the left pane.
Select View all events.
Select an event in the list to open the event dialog box.
The Event Dialog Box
The event dialog box contains information about the occurred event describing what has happened, where and when.

Position | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Heading - Describes what part of the system the event concerns. |
2 | Event name - A short descriptive text of the event. |
3 | Code - A unique four-digit number that identifies the event. |
4 | Module - Describes in what part of the system the event concerns. |
5 | Type - Information, Warning or Error. |
6 | Time - Date and time when the event occurred. |
Event Codes
Different types of events are used to notify the user of certain state changes or occurrences in the system. Each event requires a different action.
Some of the procedures described can only be performed by Atlas Copco Service personnel.
For more information about a specific event code, use the below filters or enter the event code search criteria in the search box.
Log / Display / Ack / Conf | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
none | item | none | none | none | column | list | list |
1000 | Info | Controller Started | The controller is started. | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Controller and Tool | ||
1001 | Warning | Controller Serial Number Updated | Generated at start-up if IT-board box serial number (controller serial number) differs from AUX-board box serial number. AUX-board is considered to be non-replaceable in field. The controller will reboot when the serial number is updated. | Replace IT-board or box. | Log Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller and Tool |
1010 | Info | Tool Connected | A tool is connected. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Controller and Tool | |
1011 | Info | Tool Disconnected | A tool is disconnected. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Controller and Tool | |
1012 | Info | Tool Rejected Controller Connection | This event can occur if the tool is into a skip-zone. | Verify if another controller is connected to the tool. Make sure that the tool settings are correctly set up. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller and Tool |
2000 | Warning | Battery Low | Replace battery. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2001 | Warning | Battery Empty | Replace battery. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2002 | Warning | Tool Battery Health Low | Tool battery health problem is detected. | Replace battery. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2004 | Warning | Tool is not of the preferred type | Tool has been replaced by a tool with a different Tool Max Torque. | Change tool. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2006 | Warning | Tool Backup Battery Health low | The backup battery in the tool has too poor performance. | The backup battery should be replaced. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2007 | Warning | Tool Backup Battery Missing | Tool backup battery is missing. | Insert battery | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2008 | Warning | Tool Backup Battery Error | Tool backup battery error detected. | Replace battery. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2009 | Warning | Backup Battery Voltage Low | The controller's backup battery is almost empty | Replace battery. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2010 | Error | Tool Software Version Mismatch | Tool and controller software versions not compatible. | Service tool - update tool software. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2012 | Warning | Tool Communication Disturbance | Communication between tool and controller interrupted. | Relocate antenna placement. | Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Tool |
2013 | Warning | Illegal Ring Position | Tool direction switch in faulty position. | If occurring frequently - service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2014 | Warning | Tool Overheated | Tool overheated. | Allow tool to cool down. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2015 | Error | Tool Temperature Sensor Error | SRB, TBP and IxB tools only. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2016 | Warning | Tool Pulse Unit Overheated | Pulse unit overheated. Tool is not locked, but the warning is displayed whenever the tool is started as long as the pulse unit temperature is over threshold. | Allow tool to cool down. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2019 | Warning | Tool Could not Start Motor | Tool motor failure. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2020 | Warning | Tool Requires Motor Tuning | Tool requires motor tuning. | Perform a motor tuning. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2021 | Warning | Motor Tuning Failed | Motor tuning failed. | Complete motor tuning or service the tool. | Log | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2022 | Info | Motor Tuning Completed | Motor tuning completed. | Log Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2023 | Warning | The Tool Requires Open End Tuning | The tool requires open end tuning. | Perform open end tuning. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2024 | Warning | Open End Tuning Failed | Open end tuning failed. | Try to perform open end tuning one more time. If it fails again, service the tool. | Log Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2025 | Info | Open End Tuning Successful | Open end tuning successful. | Log Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2026 | Warning | Open End Position Failed | Open end position failed. | Press the tool trigger again and wait for the positioning to be completed. If it fails again, service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2027 | Warning | Usage Limited Due To High Tool Temperature | Temperature limit value has been reached. Tightening has been inhibited to reduce risk for tool shutting down due to overheating. | Wait until tool temperature has been reduced. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2030 | Error | Tool Memory Failure: Change Tool | Tool memory corrupt. | Service the tool. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2031 | Error | Tool Accessory Memory Corrupt | Tool accessory memory corrupt. | Service the tool accessory. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2040 | Error | System Check Failure | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool | ||
2041 | Error | Torque Transducer Error | Will be generated either on calibration error or if tool reports transducer error. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2042 | Error | Angle Transducer Error | Service the tool. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2043 | Error | Tool Ground Fault Error | Service the tool. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2044 | Info | Tool Service Interval Expired | Indicates that servicing of the tool is needed. Triggered when the number of set tightenings has been exceeded. | Perform service of tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2045 | Warning | Tool Calibration Data Invalid | If validation of calibration data fails. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2046 | Info | Tool: Next Calibration Date Has Passed | Indicates that calibration of tool is needed. Triggered when calibration alarm is enabled in settings and the current time is greater than next calibration date. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2048 | Info | Tool Calibration Value Updated By QA Device | Tool calibration was updated when a calibration with a QA device was performed. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2050 | Error | Tool Parameter File Not Supported | Required tool parameters are missing. | Update tool parameters. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2060 | Info | Unexpected Trigger Behavior | Used to prevent start of tool if accessory is connected. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2071 | Error | Tool Memory Corrupt | Tool descriptor is corrupt. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2072 | Info | Unknown Device Connected | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool | ||
2073 | Warning | Tool Trigger Supervision Failure | HW channel failure. Mismatch between hardware and software of tool trigger. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2074 | Warning | Tool Indicator Board Failure | Tool indicator board failure. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2075 | Warning | Tool Fan Voltage Failure | Tool fan voltage failure. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2076 | Warning | Tool Accessory Bus Voltage Failure | Tool accessory bus voltage failure. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2077 | Warning | Tool Trigger Sensor Error | Tool trigger sensor error. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2078 | Info | Tool Tightening Program Updated | Tool locked due to tightening program update. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2079 | Error | Tool Cable Not Supported | Tool cable is corrupt. The chip in the cable is not responding or is damaged. | Switch cable. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tool |
2080 | Error | Tool Battery Failure | DC voltage too high or too low. Battery failure. | Contact the Atlas Copco service representative and send back battery to Atlas Copco (do not reuse it!). | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2081 | Error | Tool Current Limit Reached | The current limit value has been reached and the drive is disabled. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2082 | Error | Tool Current Measurement Error | Current measurement error. Current cannot be measured with a reliable result. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2083 | Error | Tool Internal Error | Various internal hardware errors. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2084 | Error | Tool Internal Software Error | Various internal software errors. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2085 | Error | Tool RBU Error | An RBU error was detected by the tool software. | Check that the RBU is correctly installed. If error is still present then service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2086 | Error | Tool Stall | Tool motor is stalling. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2087 | Warning | Tool Motor Current High | Tool motor current limit value is exceeded, and the tool is locked. Tool will enter failsafe mode. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2088 | Warning | Tool Battery Current High | Tool battery current is too high. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2089 | Warning | Tool Drive Voltage Low | Tool drive voltage is below the monitored lower voltage limit value. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2090 | Warning | Tool Drive Voltage High | Tool drive voltage is above monitored higher voltage limit value. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2091 | Warning | Tool Main Board Error | Tool main board internal error. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2092 | Warning | Tool Power Module Error | Tool power module internal error. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool | |
2093 | Warning | Pulse Unit Oil Level Low | The oil level of the connected pulse tool is low. | Service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2094 | Warning | Pulse Unit Oil Level Empty | The oil level of the connected pulse tool is below required operational level. | Service the tool. | Log Display Ack Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2095 | Warning | Tool Battery Communication Lost | Tool lost communication with battery. | Make sure battery is snugged correctly. Otherwise change battery. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2096 | Error | Tool Battery Software Version Mismatch | Tool battery software incompatible with tool software. | Update software. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2100 | Info | STwrench smartHEAD Removed | STwrench smartHEAD has been removed. | Reconnect smartHEAD and restart the wrench. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tool |
2101 | Warning | Wrench Tightening When Locked | A wrench tightening was performed when the tool status was locked in the controller. | Wait until the tool status in controller is unlocked. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 | Tool |
2120 | Warning | Unable To Start: Tool Has No Active Torque Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2121 | Warning | Transducers Are Disabled For Connected Tool | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2122 | Warning | Unable To Start: Tool Is Missing Required Torque Transducer | Log Display | Flex IxB | Tool | ||
2123 | Warning | Unable To Start: Tool Is Missing Required Angle Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2124 | Error | Torque Transducer Error On Main Transducer | Shows that there is an error on the Main torque transducer of a Tool with dual transducers. | Log Display | Flex | Tool | |
2125 | Error | Torque Transducer Error On Secondary Transducer | Shows that there is an error on the Secondary torque transducer of a Tool with dual transducers. | Log Display | Flex | Tool | |
2126 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Calibration Error On Main Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2127 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Calibration Error | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Tool | ||
2128 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer: Shunt Test Failed On Main Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2129 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer: Shunt Test Failed | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Tool | ||
2130 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer: Zero Offset Compensation Failed On Main Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2131 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer: Zero Offset Compensation Failed | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Tool | ||
2132 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Hardware Error On Main Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2133 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Hardware Error | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Tool | ||
2134 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Error: Overflow In A/D Converter On Main Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2135 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Error: Overflow In A/D Converter | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Tool | ||
2136 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Calibration Error On Secondary Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2137 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Error: Shunt Test Failed On Secondary Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2138 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Error: Zero Offset Compensation Failed On Secondary Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2139 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Hardware Error On Secondary Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2140 | Error | Tool Torque Transducer Error: Overflow In A/D Converter On Secondary Transducer | Log Display | Flex | Tool | ||
2202 | Error | Tool HMI overcurrent occurred | Tool HMI overcurrent was detected. | Service the tool. Replace tool HMI. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB | Tool |
2203 | Error | Tool front light overcurrent occurred | Tool front light overcurrent was detected | Service the tool. Replace tool front light. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB | Tool |
2204 | Error | Accessory bus overcurrent occurred | Accessory bus overcurrent was detected. | Service the tool. Replace accessory bus. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB | Tool |
2207 | Error | Vibrator overcurrent occurred | Vibrator overcurrent was detected. | Service the tool. Replace the vibrator. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB | Tool |
2208 | Warning | System CPU temperature high | System CPU temperature high. | Wait until tool temperature has been reduced. | Log Display Conf | IxB | Tool |
2209 | Error | System CPU temperature critical | System CPU temperature critical. | Wait until tool temperature has been reduced. | Log Display Conf | IxB | Tool |
2210 | Error | Unsupported power source: tightening not permitted | Battery with too low voltage attached to the tool. | Attach battery with higher voltage to the tool. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB | Tool |
2217 | Info | Running on backup battery | Running on backup battery. | Log | IxB | Tool | |
2218 | Info | Battery connected | Battery connected or controller/tool started. | Log | IxB | Tool | |
2219 | Info | Power source: unknown | Unknown power source connected or controller/tool started with unknown power source. | Log | IxB | Tool | |
2500 | Error | Tensioner puller bar max number | Tensioner puller bar must be replaced. System is locked for usage. Pressure can only be released. | Send the tensioner to service organization for replacement of the puller bar. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2501 | Error | Pump motor protection alarm | The pump motor protection has stopped the motor. The system must stop. If the system is under pressure, it needs manual actions to release pressure. | Turn off the system. If under pressure, mechanically release the pressure and send the pump to service. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2502 | Error | Pump motor oil level low alarm | The pump motor oil level is low which has stopped the motor. If the system is under pressure, it needs manual actions to release pressure. | Turn off the system. If under pressure, mechanically release the pressure and top up oil. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2503 | Error | Pump motor oil temperature high alarm | The pump motor oil temperature is high. | Turn off the system and wait for the oil to cool down. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2504 | Error | Tensioner pressure sensor alarm | Failure in the pressure sensor electronics of the tensioner. No pressure can be read nor reported to the system. | Turn off the system. If under pressure, mechanically release the pressure and send the tensioner to service. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2505 | Error | Pump pressure sensor alarm | Failure in the pressure sensor electronics of the pump. No pressure can be read nor reported to the system. | Turn off the system. If under pressure, mechanically release the pressure and send the pump to service. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2506 | Error | Unexpected clockwise rotation detected | A clockwise nut rotation while waiting for pressure release after completed tensioning. The result is invalidated. | Release pressure and tension the nut again. | Log Display Conf | PFHC | Tool |
2507 | Error | Unexpected counter clockwise rotation detected | A counter clockwise nut rotation while waiting for pressure release after completed tensioning. The result is invalidated. | Release pressure and tension the nut again. | Log Display Conf | PFHC | Tool |
2508 | Error | Pump or tensioner pressure sensor failure | Too large difference between the pressure sensor readings in the pump and the tensioner. Pressurization is halted. | Problem in the hydraulics or the calibration of the pressure sensors. Restart the system and try again. If the problem repeats, contact your local Atlas Copco sales representative. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2509 | Error | Tensioner pressure sensor failure or hydraulic hose failure | The tensioner's pressure sensor indicates no pressure but the pump's sensor reads a pressure increase. Pressurization is halted. | Problem in the hydraulics or the calibration of the pressure sensors. Restart the system and try again. If the problem repeats, contact your local Atlas Copco sales representative. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2510 | Error | Set custom ID failed | Setting custom ID failed. | Restart the system and check the connected devices. If Custom ID for the unit is wrong, redo the setting. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2511 | Info | Custom ID is set | Setting custom ID succeeded. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool | |
2512 | Warning | Malformed Barcode string, ignored | The scanned string could not be parsed as a tower data bar code. | Scan a proper tower data qr code or scan tower section id. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2513 | Error | No pump pressure detected | The system is trying to pressurize but no pressure increase is registered in the pump. Possible cause is incorrect phase order in the three phase connector. | Power off the system and reverse the phases of the power connector. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2514 | Warning | Tensioner overtorque alarm | Too high torque is applied to the click wrench. This causes damage to the torque sensor. | Relax the torque. | Log | PFHC | Tool |
2515 | Warning | Tensioner overpressure alarm | The pressure in the tensioner is too high. | Let the pressure drop, or release the pressure. Check the hydraulic pressure parameters. | Log | PFHC | Tool |
2516 | Warning | Unexpected Pump or Tensioner firmware | Unexpected Pump or Tensioner firmware version detected, restart system. If the problem persists, the system may be possible to run, but carefully observe any unexpected behaviour. | Power cycle system | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
2517 | Error | Incompatible Pump or Tensioner firmware version, restart system. The system cannot run. | Incompatible Pump or Tensioner firmware version, restart system. The system cannot run. | Restart system, if this doesn’t help replace the failing unit. Check connected devices to see which one has not connected. | Log Display Ack | PFHC | Tool |
3000 | Error | Controller Internal Software Error | Software error in the controller. | Contact service. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3001 | Error | Controller Clock Battery Empty | Internal battery is getting close to end of life. | Replace battery. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3010 | Warning | System Overheated | The controller is overheated. | Cool down. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3011 | Warning | Drive Overheated Controller Hardware | Cool down. | Log Display Conf | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3013 | Warning | Usage Limited Due To High Controller Temperature | Temperature limit value has been reached. Tightening has been inhibited to reduce risk for controller shutting down due to overheating. | Wait until controller temperature has been reduced. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3020 | Warning | Controller Hardware Failure | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3021 | Warning | System Voltage Problem | DC voltage too high or too low. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3022 | Warning | Controller Voltage Problem: AC Input Voltage Too High | DC voltage too high or too low. | Fix the input voltage. | Log Display | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3023 | Warning | Controller Voltage Problem: AC Input Voltage Too Low | DC voltage too high or too low. | Fix the input voltage. | Log Display | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3024 | Warning | Drive Voltage Problem: AC Input Voltage Too High | DC voltage too high or too low. | Fix the input voltage. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3025 | Warning | Drive Voltage Problem: AC Input Voltage Too Low | DC voltage too high or too low. | Fix the input voltage. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3030 | Error | IP Address Conflicting With Another Node On The Network | The set IP address is in use by another device on the same network. | Change IP address on one of the devices. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3031 | Info | Network Cable Unplugged | The carrier of the factory port is lost (cable disconnected). | Check the cable connection. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3032 | Info | Pairing Started | Tool pairing started. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3033 | Info | Pairing Successful | Tool pairing successful. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3034 | Info | Pairing Unsuccessful: No Tool Found | The controller found no tool to pair with when scanning for radio peers. | Set the tool in pairing mode and try again. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3035 | Error | Pairing Unsuccessful: More Than One Tool Found | The controller found more than one tool when scanning for radio peers. | Ensure that only one tool is in pairing mode when starting the pairing mode on the controller. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3036 | Error | Pairing Unsuccessful: Communication Error | The controller experienced a loss of connection, an unexpected answer or timeout during the pairing process. | Try to perform pairing one more time. If it fails again, service the tool. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3037 | Info | Pairing Unsuccessful: Tool Slot Is Full | Clear one tool slot. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3040 | Warning | Emergency Stop | Drive disabled due to emergency stop. | Reset emergency stop. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3050 | Info | System Clock Updated | System clock has been updated. | Log Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3051 | Error | System Clock Error | Wrong time read from hardware Real Time Clock (RTC). | Change RTC battery. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3052 | Warning | Remote Start Configuration Error | Mismatch between HW and SW remote start configuration. | Verify that HW dip switch matches the selected start source. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3053 | Info | Drive Connected | StepSync drive has been connected. | Log Display | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3054 | Info | Drive Disconnected | StepSync drive disconnected. | Log Display | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3055 | Warning | Mode Configuration Error | Generated when selected mode is configured wrongly. E.g. configuring two bolts with the same bolt number or the same channel, incomplete mode configuration. | Check ToolsTalk 2 for mode configuration error. | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3056 | Warning | Unable to Start: Tool Or Drive Is Missing | Generated when a used channel is missing a drive or tool. | Verify Channel Menu on the HMI. Connect missing drive or tool. | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3057 | Info | Unable to Start: Channel Is Already In Use | Generated when a needed channel has been allocated to another virtual station. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3058 | Info | No Mode Selected | Select mode. | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3059 | Warning | Failed To Connect To Atlas Copco License Manager | Indicates that the controller failed to connect to the local license manager to get licenses. | Verify the local network. If it fails again, service the controller. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3061 | Warning | Unable To Start: Enable Signal Is Low | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3062 | Warning | Unable To Start: Stop Signal Is High | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3063 | Warning | Unable To Start: All Channels Inhibited | All channels have been set inhibited, so no tightening can be started. | Set at least one channel to not be inhibited. | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3064 | Warning | Carrier Number Faulty | A FlexCarrier hex switch is set to zero. | Turn the switch to a non-zero value. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3065 | Warning | Carrier E-Stop Configuration Plug Wrong Type Or Missing | A Carrier is missing its E-stop configuration plug, or the plug type is wrong. | Insert correct plug type. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3066 | Warning | Carrier Voltage Inlet: No 3-Phase AC | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3067 | Warning | Carrier Voltage Inlet: One AC Phase Missing | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3068 | Warning | Carrier: Internal 24 VDC Power Supply Unit Broken | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3069 | Warning | Carrier 24 Voltage OUT-Port Disabled Due To Over-Current | Reset the system. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3070 | Warning | Carrier, Hardware Error In PF6 FlexControl Cable OUT | Reset the system. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3071 | Warning | Carrier, Hardware Error In PF6 FlexControl Cable IN | Reset the system. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3072 | Warning | Emergency Stop 24 VDC Power Failure Due To Short-Circuit | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3073 | Warning | Unable To Start: System Is Emergency Stopped | When allocating multiple spindles, this event is invoked by "preStartCheckFailed" due to emergency stop. | Reset the emergency stop. | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3074 | Warning | Carrier Overheated | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3075 | Warning | Carrier Temperature OK | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3076 | Warning | Carrier: Internal 24 VDC Power Supply Overload | Current output from internal PSU is too high. | Disconnect other carriers that are powered from the PSU. Disconnect any external equipment using 24 VDC. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3077 | Warning | Carrier: Internal 24 VDC Power Supply Over Voltage | Voltage output from internal PSU is too high. | Replace the carrier. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3078 | Warning | Carrier: Internal 24 VDC Power Supply Under Voltage | Voltage output from internal PSU is too low. | Replace the carrier. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3079 | Warning | External Supply To Carrier: 24 VDC Over Voltage | Backup input voltage is more than 27 VDC. | Adjust the backup input voltage. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3080 | Warning | External Supply To Carrier: 24 VDC Under Voltage | Backup input voltage is less than 19 VDC. | Adjust the backup input voltage. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3081 | Warning | Carrier Voltage Inlet: 3-Phase AC Over Voltage | Input voltage is too high. | Lower input voltage: must be 400 VAC or 480 VAC. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3082 | Warning | Carrier Voltage Inlet: 3-Phase AC Under Voltage | Input voltage is too low. | Higher input voltage: must be 400 VAC or 480 VAC. | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3083 | Error | Wrong Anybus/Profisafe Module Firmware | Log Display | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3084 | Error | Soft PLC Runtime Error | eCLR has terminated in an uncontrolled way. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3085 | Warning | Carrier: Fan Module Out Of Order | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3086 | Warning | Carrier: Fan Module Partly Out Of Order | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3087 | Warning | Carrier: Left Fan Module Out Of Order | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3088 | Warning | Carrier: Left Fan Module Partly Out Of Order | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3089 | Warning | Carrier: Right Fan Module Out Of Order | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3090 | Warning | Carrier: Right Fan Module Partly Out Of Order | Log Display | Flex | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3096 | Warning | Cellular signal strength low | The RSSI value for the cellular connection is under the defined threshold value of -98 dBm. | Move the tool closer to the cellular antennas for a stronger connection and avoid data loss. | Conf | IxB | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3097 | Warning | Cellular connection lost | The system lost connection to the cellular network. |
| Log Display Conf | IxB | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3100 | Warning | Mode Configuration Does Not Exist | Log Display | Flex StepSync | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3150 | Error | Software IAM Incompatibility | IAM is incompatible with the software that is installed on the controller. | Replace IAM. | Log Display Ack | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3160 | Error | Failed To Activate Newly Installed Software | Something went wrong during the activation. When the newly installed software starts, a fallback to the previous working software happens. This error happens when the new software fails to start for three times and only during software installation. | Take an export and contact Atlas Copco for further assistance. Note down the software version you are trying to install as well as the software version that is working. | Log Display Ack | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3161 | Error | Started On Unexpected Software Partition | The controller has started on the inactive software side and not on the expected software side. | Note down the software information (on the Home screen of the controller, select Controller > Software). Try to restart the controller and make sure its running on correct software when started again. If error persists, do an export and contact Atlas Copco. | Log Display Ack | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3500 | Error | Generic License Manager Error | Inconsistency detected in the feature management system used. | Contact Atlas Copco representative. | Log Display Ack | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3501 | Error | License Manager Synchronization Error | Log Display Ack | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3502 | Info | License Manager Synchronization Done | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |||
3503 | Warning | License Manager: Another Source in Use | License is used by another source. | Verify license assignment. | Log Display | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3504 | Warning | License Manager Restart Needed | Restart license manager. | Log Display | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3505 | Info | USB License Synchronization Started | Log | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3506 | Error | USB License Synchronization Error | Log | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3507 | Info | USB License Synchronization Done | Log | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 | Controller, Drive and StepSync | ||
3508 | Info | One or more of your licenses are about to expire. Please make sure you have a license server configured | Update licenses. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3511 | Warning | One of your licenses has a different license definition | Inconsistency detected in a license to be used. | Contact Atlas Copco representative. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync |
3550 | Warning | License Is Missing | Install the correct license. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
3551 | Warning | Wireless Communication Disabled By Licensing | Unassign Standalone license from the Virtual Station. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Controller, Drive and StepSync | |
4010 | Info | Tool Locked By Digital Input | The tool is locked by a digital input signal. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4011 | Info | Tool Locked By Open Protocol | The tool is locked by Open Protocol. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4012 | Info | Tool Locked By Fieldbus | The tool is locked by the Fieldbus. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4013 | Info | Tool Locked By Socket Selector | Tool is locked when the socket selector is disconnected from the Virtual Station. | Unlock by Master Unlock. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process |
4014 | Info | Tool Locked By Soft PLC | Soft PLC signal locked the tool. | Unlock by Master Unlock. | Log Display Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process |
4015 | Info | Loosening Disabled | Loosening is disabled in the tightening program. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4016 | Info | Tightening Disabled | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4017 | Info | Loosening Not Configured | Loosening is not configured in the selected tightening program | Select different tightening program. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process |
4020 | Info | Too Many NOK Tightenings | Maximum consecutive NOK tightenings in batch is exceeded | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4025 | Info | No Tightening Program Selected | No tightening program selected. | Select tightening program or batch sequence. | Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process |
4030 | Info | Batch Sequence Aborted | The batch sequence has been aborted. | Log Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Tightening Process | |
4031 | Info | Max Time To Complete Batch Sequence Reached | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4032 | Info | Max Time To Complete First Tightening Reached | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4035 | Info | Locked By Line Control | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4040 | Info | Locked By Alternative Identifier | Tool locked by alternative identifier. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4050 | Invalid Socket Configuration | Tightening program assigned to multiple sockets. | Tightening program assigned to multiple sockets. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4060 | Info | Tool Locked On Batch Complete | When running a batch with flag Tool lock on batch sequence complete this event is generated when the user press the trigger. | Unlock with signal Unlock Tool on complete. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process |
4070 | Info | Process Enter Manual Mode | Indicates that manual mode has been activated for a virtual station. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4071 | Info | Process Enter Automatic Mode | Indicates that automatic mode has been entered for a virtual station. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4072 | Info | Test Bolt | Conf | Flex StepSync | Tightening Process | ||
4073 | Info | Tool zero position updated | Indicates that the tool zero position is set using signals. | Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4100 | Warning | Identifier Not Accepted: Invalid String Length | Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4101 | Warning | String Selection Unsuccessful: Multiple Matches | Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4102 | Warning | String Selection Unsuccessful: No Match Found | Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4103 | Warning | Identifier Not Accepted: Identical String Already Received | Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4104 | Warning | Identifier Not Accepted: No Match Found | Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4500 | Info | Result DriveError | Internal driver error or driver loss detected. | Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4501 | Info | Result Rehit | Attempt to tighten an already tightened bolt when Rehit detection is on. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4502 | Info | Result Soft Start Torque Low | Soft start torque below minimum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4503 | Info | Result Soft Start Torque High | Soft start torque exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4504 | Info | Result Self Tap Torque High | Self-tap torque exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4505 | Info | Result Self Tap Torque Low | Self-tap torque below minimum limit. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4506 | Info | Result Safety Torque Low | Automatically calculated torque value to ensure torque sensor is mounted correctly. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4507 | Info | Result Rundown Torque High | Rundown torque exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4508 | Info | Result Rundown Angle High | Rundown angle exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4509 | Info | Result Rundown Time High | Rundown time exceeded maximum limit. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4510 | Info | Result Rundown Time Low | Rundown time below minimum limit. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4511 | Info | Result Rundown Torque Low | Rundown torque below minimum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4512 | Info | Result Rundown Angle Low | Rundown angle below minimum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4513 | Info | Result Final Torque High | Final step torque exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4514 | Info | Result Final Angle High | Final step angle exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4515 | Info | Result Final Torque Low | Final step torque below minimum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4516 | Info | Result Final Angle Low | Final step angle below minimum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4517 | Info | Result Tightening Timeout | Tightening time limit exceeded. For General Tightening Strategies max tightening time is 30 seconds. For Multistep max tightening time depends on step restriction Maximum Time Limit. Error code is dependent on tightening stage. | Redo tightening. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process |
4518 | Info | Result Trigger Lost | Tool trigger was released before target was reached. For General Tightening Strategies it is not allowed to release the trigger before the tightening stage has finished. For Multistep, the error is displayed when trigger is lost before the target in a specific step is reached. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4519 | Info | Premature Torque Loss | Socket has slipped off the nut. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4520 | Info | Result Target Reached Before Final Step | Target torque reached before final step in tightening program. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4521 | Info | Result Post View Torque Low | Post view torque below minimum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4522 | Info | Result Post View Torque High | Post view torque exceeded maximum level. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4523 | Info | Result Post View Torque Interval Not Reached | Post view torque interval not reached. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4524 | Info | Result Torque Compensation Interval Not Reached | Torque compensation interval angle before rundown end not reached. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4525 | Info | Result Tool Movement Exceeded | From a NOK tightening detailed status. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4526 | Info | Result SafetyCurrMon Sensor Mismatch | Current monitoring error. | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4527 | Info | Result Tool Movement Exceeded | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |||
4538 | Info | Result Final Supervision Torque Low | Final Supervision Torque was not reached. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4543 | Info | Result Snug Monitor High | Wrench only. Monitor detected snug value exceeded. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4545 | Info | Result No Residual Torque | Wrench only. Residual torque was under threshold. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4546 | Info | Result Overspeed | Wrench only. Wrench gyro failed to measure angle due to high speed. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4547 | Info | Result Effective Loosening | Wrench only. Wrench detected unexpected loosening. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4548 | Info | Result Final Less Than Target | Final torque is below target torque set in tightening program. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4549 | Info | TurboTight Time Limit Exceeded | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4550 | Info | Result Rundown Pulses High | Maximum number of rundown pulses is exceeded. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4551 | Info | Result Rundown Pulses Low | Rundown is completed before the minimum number of rundown pulses is reached. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4552 | Info | Result Final Pulses High | Maximum number of pulses is exceeded. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4553 | Info | Result Final Pulses Low | Tightening is completed before the minimum number of pulses is reached. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4554 | Info | Current At Shutoff High | Current at shut off exceeded Current Limit High. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4555 | Info | Current At Shutoff Low | Shut off current measured was below Current Limit Low. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4556 | Info | Uncategorized Multistep Error | An error in the multistep configuration, often with tool validation. | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | |
4557 | Info | Result Overload | Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Tightening Process | ||
4600 | Warning | Data Drop or Data Hold used in combination with Batch Tightening. The signals have no effect | Data Drop and Data Hold are only supported for worktasks, without batch control. Select another worktask if the signals must be used. | Flex StepSync | Tightening Process | ||
4601 | Info | Data Hold Active: tightening result is sent once signal is low | Flex StepSync | Tightening Process | |||
4602 | Info | Data Drop active: tightening result discarded | Flex StepSync | Tightening Process | |||
5010 | Warning | Invalid Tightening Program Parameter Value | The parameter in the selected tightening program are invalid. | Check the configuration of the selected tightening program to find and to change the value of the parameter. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Program Configuration |
5011 | Warning | Couldn't prepare program storage in tool | It is not possible to read the current program storage size in the STB tool, or to prepare the program storage for downloading the updated - or newly selected - tightening program to the STB tool. |
| Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Program Configuration |
5020 | Info | Main Trigger Is Not The Active Start Source | Generated when configured for push start only and user presses main trigger. Will be generated until user presses the push start. | Press push start to start the tool. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Program Configuration |
5030 | Info | Tightening Program Complexity Exceeds Tool Capacity | The selected tightening program is too complex for the STB tool that is used. Tool will be locked. | Reduce complexity of the tightening program, or choose different program. | Log Display Conf | Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Program Configuration |
6010 | Info | Accessory Connected | Accessory is connected to the controller. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Accessory | |
6020 | Info | Accessory Disconnected | Accessory is disconnected from the controller. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Accessory | |
6021 | Warning | Fieldbus Offline | No communication with Fieldbus. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Accessory | |
6030 | Warning | Accessory Address Collision | Two or more accessories with the same address are connected. | Change address on accessory. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Accessory |
6040 | Warning | Accessory Communication Error | Intermittent communication error with accessory. | Check cables and connectors. | Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Accessory |
6041 | Warning | Fieldbus Error | Communication error with Fieldbus. |
| Log Display Ack Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync | Accessory |
6042 | Warning | Fieldbus Module Mismatch | The installed Fieldbus module does not match with the configured module. | Change the configuration to match with the installed module, or replace the installed module with the correct one. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync | Accessory |
6043 | Warning | Fieldbus Output Buffer Overflow | The output buffer used for the Fieldbus communication is exhausted and an overflow of the buffer has occurred. One or more signal updates have been discarded. | Stop Fieldbus communication and Fieldbus diagnostics (if used) to recover the buffer. If this event occurs frequently, check your Fieldbus communication setup, including the PLC program: too frequent updates compared to your update interval can lead to this scenario. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync | Accessory |
6044 | Warning | Fieldbus Provider ID mismatch | The installed fieldbus module is not supported. | Connect a supported Atlas Copco fieldbus module. | Log Display Ack | Power Focus 8 | Accessory |
6050 | Info | Wrong Socket Selected | Generated when no or incorrect socket is selected. | Log Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Accessory | |
6090 | Warning | Barcode Scanner Could Not Be Identified | When no unique serial number is found. | Configure the barcode reader device. | Log Display Ack Conf | Flex Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Accessory |
7010 | Info | Message Text To Display | General event for displaying of messages. | Display Ack Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC PFHC | Message | |
8200 | Info | Failed To Open Serial Port | Serial port to be used could not be opened. | Check serial port connections. | Display Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Miscellaneous |
8300 | Warning | Open Protocol client communication timed out | Communication to an Open Protocol client has timed out. No keep alive message or command sent within expected time. |
| Log Display Conf | Flex IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 StepSync Power Focus XC | Miscellaneous |
8214 | Error | EHMI Software Version Mismatch | EHMI software version does not match in compatibility with the controller. | Update the software version of the EHMI. | Log Display Ack Conf | IxB Power Focus 6000 Power Focus 8 Power Focus XC | Miscellaneous |
Glossary
List of products for which the event code is available.
Group which the event codes belong to.
A short description of the event and why it occurs.
If applicable, the procedure contains an instruction on how to clear the event.
Tells the user whether the event is to be saved in the event log or not. The value in this list is the default value.
Tells the user whether the event is to be displayed on the screen or not. The value in this list is the default value.
Tells the user whether the event must be acknowledged or not before you can proceed. The value in this list is the default value.
The unique event number.
Type of event: Info, Warning, and Error.
A descriptive name of the event.
Working with the Settings Tab
Network Configurations
The tool can be set up to be accessed wirelessly from a web browser on a Local Area Network (LAN), using IPv4 protocol.
There is an option to use the tool as a client or an access point for other devices.
Open the cover of the hand controller's USB connection port.
Connect a PC to the USB-C connector on the hand controller. To make sure that the PC gives enough power to the hand controller, use the USB-3.0 ports.
To enter the Configuration GUI, enter the following address in your browser: 164.254.1.1/config.html.
See more information in the section Web Browser Requirements.
Configuring Channels
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Network in the left pane.
In the Channels field, choose frequency (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) and select Edit.
Choose to enable or disable channels.
Configuring a Wireless Client
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Network in the left pane.
In the Wireless Client field, select Edit.
Set Enabled to On.
Set DHCP to On or Off depending on the configuration. If set to Off, fill out the required information, provided by the local system administrator:
IP address
Subnet mask
Gateway
Enter a Network name (SSID).
In the Security field, select Mode and choose a security mode from the list. If WPA2 Personal is chosen, enter a Security key.
Enter security parameters and import cert files and keys, as applicable.
Edit the Optional Settings as applicable.
Select Apply.
The tool will establish a wireless connection to the network, indicated with the tool's blue connection LED indicator emitting a steady light.
To access the user interface wirelessly, type the IP address into a web browser.
Configuring the Tool as a Wireless Access Point
If multiple channels have been configured previously in Wireless Client mode, enabling Wireless AP mode will update the channel list to contain only the current/default channel for the Wireless AP mode.
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Network in the left pane.
In the Wireless AP field, select Edit.
Set Enabled to On.
Enter the required information, provided by the local system administrator:
IP address
Subnet mask
Gateway
To distribute IP addresses, set DHCP Server to On and enter IP range start and IP range stop.
Enter a Network name (SSID).
In the Security field, select Mode and choose a security mode from the list. If WPA2 Personal is chosen, enter a Security key.
Select Apply.
Server Connections
The hand controller can be set up to communicate with servers running the following Atlas Copco software product:
ToolsNet − used to handle result reporting.
Configuring the ToolsNet Connection
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Server Connections in the left pane.
In the ToolsNet field, set the following parameters:
Field
Description
On/Off
Enables/Disables communication with the ToolsNet server
Server port
ToolsNet server port
Server host
ToolsNet server IP address
Select Apply.
To view the ToolsNet connection status, go to Reports > Results and select the  button. In the appearing dialog box, select the Server connections tab.
button. In the appearing dialog box, select the Server connections tab.
For information on how to configure ToolsNet, refer to the ToolsNet 8 User Guide.
Configuring the Remote Logging Connection
To connect a controller to a remote logging server, configure and activate the remote logging settings on the controller.
On the home view, go to the Settings tab and select Server connections on the left pane.
On the Remote Logging window, configure the following parameters:
Field | Description |
|---|---|
On/Off | Enables/Disables communication with the remote logging server |
TCP/UDP | Selects TCP or UDP protocol |
Server host | Remote logging server IP address |
Server port | Remote logging server port |
Configure Log Levels
To configure the logs that are stored on the remote logging server:
On the home view, go to the Settings tab and select Server connections on the left pane.
On the Remote Logging window, select Configure.
On the Configure Facilities window, select the applicable checkboxes.
Category
SysLog classification
Error
Alert, Critical, Emergency, Error
Warning
Warning
Info
Informational, Notice

To restore the selection to the previous configuration, select UNDO.
Select Apply.
Preferences
Date and Time
Date and time must be set in order for events and results to get the correct time stamp for when they occurred. The time is retrieved from one of three available sources:
Manual − the date, time, and time zone are set manually.
NTP − the date and time are retrieved from an NTP (Network Time Protocol) server defined in the user interface.
ToolsNet − the date and time are retrieved from the ToolsNet server.
A functional network connection is required for the NTP and ToolsNet time sources.
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Preferences in the left pane.
In the Date and Time field, set the following parameters:
Parameter
Description
Source
Source to retrieve the time from.
NTP Server 1
IP-address of an NTP server providing date and time for the tool.
Server 1 status
OK/No Status
NTP Server 2
IP-address of an NTP server providing date and time for the tool.
Server 2 status
OK/No Status
Date
Date entered manually if the source is set to manual.
Time
Time entered manually if the source is set to manual.
Time zone
The time zone; either the location or a standard time zone such as UTC (coordinated universal time)
Select APPLY.
Setting Language
The user interface is available in the following twelve languages:
English
Czech
German
Spanish
French
Korean
Italian
Japanese
Portuguese
Russian
Swedish
Chinese
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Preferences in the left pane.
In the Language field, select the language currently in use and choose a language from the list.
The language change will take effect immediately.
Setting the Torque Unit
Torque results are displayed in the chosen unit both after a tightening is performed and when stored in the results list.
Unit | Description |
|---|---|
cNm | centinewton metre |
dNm | decinewton metre |
Nm | newton metre |
kNm | kilonewton metre |
in·lbf | inch-pound force |
ft·lbf | foot-pound force |
in·ozf | inch ounce-force |
ft·ozf | foot ounce-force |
gf·cm | gram-force centimetre |
kgf·cm | kilogram-force centimetre |
kgf·m | kilogram-force metre |
Pressure Units
Go to Settings in the home menu and select Preferences in the left pane.
In the Pressure Units field, select the unit Bar or Pa from the list.
Configuration of the PIN Settings
The PIN code prevents unauthorized usage of the Web GUI or accidental changes.
If enabled, a PIN code is required when making configuration changes from the Web GUI.
Configuring the PIN
It is possible to have one or many different PIN configurations on the Web GUI. Users can decide whether or not to activate one or several PIN configurations at the same time.
Each PIN configuration has a PIN code, a user name, a switch for enabling or disabling the user/PIN, and a list of available configurations that the user can access.
When PIN is enabled and the screen is locked, a locked padlock icon is shown at the upper-right corner of the GUI. The user can access and make changes only to the selected configuration(s) without entering any PIN code, and browse the unselected configurations with read-only access only. The unselected configurations are greyed out or disabled.
The screen lock goes automatically on after a certain time of inactivity, configurable by the user.
The minimum value of the inactivity time is 20 sec and the maximum value is 600 sec. The inactivity time is configurable and applies to all PIN configurations.
After a system startup, the controller is locked if the PIN is turned on, regardless of the current inactivity time.
The users and PIN configured apply also to the Service Port (169.254.1.1).
To enable PIN protection on the Service Port, in the PIN windows, set Use PIN for Service Port to On.
Each controller can configure up to 10 users.
The PIN of each configuration has to be unique. It is required to have at least one configuration to enable the PIN functionality on the controller.
The PIN can be configured from the Web GUI.
Adding New Users
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select PIN.
In the PIN window, select Configure.
Select the Plus icon at the upper-right corner of the GUI.
The PIN-Users window shows the new user. If there are not users stored in the Web GUI, the new user is the first and only one in the list; if there are existing users stored in the Web GUI, the new user is the last of the list.Select the new user.
The User window appears.
Enter the Name and the PIN of the new user, and then confirm the PIN.
The User Name must be unique.
The Name text box can be 1 to 32 characters long.
The PIN code must have 4 digits in length (numbers 1 through 9).
Enter PIN box and Confirm PIN box need to match for the changes to be applied. By default, dots are indicated in both the text box, but these are just placeholders and need to be replaced with actual PIN codes.Select Permissions. The list of the available configurations appears.
Select the check box at the left of the necessary configuration(s) the user can access and make changes.
After selecting the necessary configuration(s), select OK.
The User window appears.
Select all selects all the available configurations at the same time.
Select Deselect all to clear the check boxes and undo the selection.
The user can access and make changes only to the configuration(s) selected in the Permissions window, and browse the unselected configurations with read-only access. For the unselected configurations, no changes are allowed.
In the User window, select Apply.
Enabling Users
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select PIN.
In the PIN window, select Configure.
In the PIN-Users window, select the check box at the left of the user name to be enabled.

PIN can also be enabled by clicking on the user name and setting - in the User window - the Enabled switch to On.
Activating the PIN configuration
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select PIN.
In the PIN window, select Configure.
In the PIN-activating window, set the PIN Code switch to On.

The PIN can only be activated when at least one user/PIN is enabled. If no user/PIN is enabled, a Warning pop-up window appears.
Enter the Inactivity Timeout (in seconds), that defines the slot of time after which the screen is automatically locked up.

Default value for Inactivity Timeout is 120 seconds: this is a global setting, and cannot be set on a per user basis.
Unlocking the Web-GUI
On the Home view, select the Padlock icon at the upper-right corner of the GUI. A pop-up window with a numeric keypad appears.
Enter the configured PIN code and select OK.

When the PIN is enabled and the screen has been unlocked, an Open Padlock icon appears at the upper-right corner of the GUI. The Web-GUI can be locked again manually, by selecting the Open Padlock icon.
Disabling Users
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select PIN.
In the PIN window, select Configure.
In the PIN-Users window, deselect the check box at the left of the user name to be disabled.

PIN can also be disabled by clicking on the user name and setting - in the User window - the Enabled switch to Off.
Deleting Users
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select PIN.
In the PIN window, select Configure.
In the PIN-Users window, select the Delete icon at the right of the user name to be deleted.

If the User is removed, also the PIN is deleted. It is not possible to access any configuration through the deleted PIN.
Configurations of the Events Settings
It is possible to configure the events available in the controller as either or several of:
Acknowledged
Logged
Displayed
Configuration of the Extended Logging
The PFHC automatically creates logs and stores them. These logs can be configured to include extended logging using log groups.
Configuring the Log Groups
The default setting for a log group is off. To change the setting of a log group to on:
On the home view, go to the Settings tab and select Extended Logging on the left pane.
On the Log Groups window, set the group to ON.
Reset Log Groups
It is possible to reset all log groups to their default settings.
On the home view, go to the Settings tab and select Extended Logging on the left pane.
On the Reset Log Groups window, select Reset.
A pop-up window appears asking if you want to reset all log groups. Select YES.
Persistent Log Groups
The log groups resets to their default setting at every reboot. To prevent resetting use persistent log groups.
On the home view, go to the Settings tab and select Extended Logging on the left pane.
On the Keep Selection after Restart window, set Persistent to ON.
Reset
Factory Reset Controller
It is possible to undo the controller to the original factory settings.
All settings, events, configurations and historical data are deleted when the controller is reset. Do a factory reset only when you are completely sure that this is required.
Performing a Controller Factory Reset
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select Reset.
In the Factory Reset Controller window, select Reset.
A pop-up window appears warning that all data will be deleted. Then, select Yes.
The controller restarts to activate the new settings.
Clear Results
It is possible to delete results and events stored on the controller.
Deleting Results and Events
On the Home view, select the Settings Tab. Then, on the left, select Reset.
In the Clear Results window, select Clear.
A pop-up window appears warning that all results and events will be deleted. Then, select Yes.
Turn off the controller and wait for 30 seconds before turning it on again.
Working with the Help Tab
This section provides help when working in Web GUI. The Power Focus HC User Manual is embedded in this tab. The chapters are in the left panel.
Operation
In this section, you can find step-by-step information about how to operate the product.
Controller GUI
System Start
The Tasks menu on the hand controller is grayed out during startup, which means that it is unavailable until the system start is completed.
During the system start, the following occurs:
The pump and the tensioner start and establish the communication with the hand controller.
If the firmware version of the pump or the tensioner is not compatible with the software version of the hand controller, the firmware version will be updated to a compatible version. This process can be observed on the LED of the tensioner, which is blue during the firmware compatibility check and the possible update process. When the tensioners status LED has stopped blinking and is steady white the tensioner has established connection with the hand controller.
If the firmware of the pump or tensioner is not what the hand controller expects the event 2516 “Unexpected Pump or Tensioner firmware version detected, restart system. If the problem persists, the system may be possible to run, but carefully observe any unexpected behaviour." is triggered. In case any reported firmware is on the hand controller’s list of incompatible firmware versions the hand controller emits event 2617 “Incompatible Pump or Tensioner firmware version, restart system. The system cannot run”. In case of incompatible firmware the hand controller will not activate Home->Tasks. In both cases restart the system and let the unit that failed to update have another go.
The hand controller Name can be replaced in the IAM, see the section Intelligent Application Module.
Connection Status
The icons for wireless connection status and ToolsNet connection status show a live update of the state of the connection. The hand controller will connect to Wifi if it is configured to do so in Settings -> Network.
When wireless is connected and the HC has an active connection to the Wifi network the Wifi connection icon appears without the diagonal line.
When the hand controller is configured for connection to ToolsNet the state of the icon reflects the state of the connection. The diagonal line means that there is no open connection to ToolsNet.
Home screen
When all three components completed the upstart process and the system communication is started, the Tasks menu is available.
Warnings and reminders
When the system has a warning or information message related to pump or tensioner status the connected devices icon is highlighted with a blue frame and the number of messages is displayed. When entering the connected devices tab the information or warning icon shows the user where additional information is available. Some statuses also show as warning banners in the home screen.
Oil change reminder
When the time for next oil change is less than four weeks, or the motor runtime has reached the 50 last hours, an oil change reminder is displayed.
The last 28 days before the next oil change date and the last 50 hours of motor runtime the info icon is displayed.
The info icon becomes a warning when the oil change date has passed, or the motor on time has reached the limit.
Working with the Tasks Tab
The Tasks menu is available when both the pump and the tensioner are connected to the hand controller.
Only tasks that have valid configurations are shown on the hand controllers GUI.
For example, if there are no configurations for Assembly, then neither Assembly nor Batch Assembly are available.
Manual mode is always present.
Assembly and Bolt Service allow one run for one bolt, for example for training or testing purposes.
The following tasks are available on the hand controller:
Assembly: a singular run of a Step tensioning configuration.
Batch Assembly: runs a batch job of a Step tensioning configuration. The operator must enter additional information before starting this job.
Manual mode: allows manual control of the tensioning process. This process can be run by any tensioner.
Bolt Service: a singular run of a bolt service configuration.
Batch Bolt Service: runs a batch job of a Tensioning Service configuration. The operator must enter additional information before starting this job.
Use Manual mode to de-tension or loosen bolts. It is recommended to use an applicable loosening strategy. For more information about de-tensioning, see section De-tensioning the Nut.
Tensioning Operations Simplified GUI
There are two hand controller GUI screens for tensioning operations, a full GUI and a simplified GUI.
The full GUI shows the measured values of pressure, torque, angle and the force that is applied on the flange.
The simplified GUI is a cleaner operator GUI similar to the LEDs on the tensioner, so the LEDs on the hand controller show the same status as the LEDs on the tensioner.
It is possible to toggle between these two GUI screens by using the up and down buttons on the hand controller.
Assembly
In Assembly tab, there is a list of pre-configured tensioning programs compatible with the connected tensioner. If no compatible programs are available, the following message appears at the bottom of the screen: No compatible program.
On the Home view, go to Tasks > Assembly.
Select a program to run by using the up and down buttons to navigate through the list and then press the Enter button in the middle to confirm the choice.
The name presented in the list is taken from the Name field under General Settings > Properties tab.
When the message Position tool on bolt appears on the screen, rundown the tensioner straight on top of the bolt.

Make sure that the socket is aligned with the nut.
Press the Forward button on the keypad to start the tensioning operation.
Tensioning Operation
Tensioning operation consists of the following phases:
Installation check
Pressurization phase
Nut tightening
Aborting can be done anytime during tensioning operation.
When the system waits for the user to take action, a help text appears after a few seconds and it disappears as soon the expected action is detected.
Installation Check
The purpose of installation check is to create a reference point for the angle measurement.
Press the pressurize button to prevent the tensioner from rotating during installation check.

The pressure may undershoot, especially in the first runs after a long break. In that case press the pressurize button again.

The pressure may overshoot - the system prompts the user to release pressure and try again.
Overshooting can happen due to the parameter Angle reset force, see section Tensioning Parameters.
Turn the nut clockwise to achieve the torque level set in the parameter Installation check torque(default value 20 Nm). Keep the torque for at least Installation check torque duration (default value 1 second).
All 3 LEDs turn green.
Release force on the click wrench.
Pressurization Phase
Press and hold the pressurize button.
When a LED on the angle row on the tensioner and its equivalent on the hand controller is lit, rundown the nut following the elongation of the bolt.

Do not apply any torque to the nut before the target pressure is reached. The pressure will do the work.
Nut Tightening
Keep the pressurize button pressed to allow the system to keep the pressure above the Min bolt tensioning pressure parameter.
The pressure will drop slowly, the system will pressurize before it drops below the minimum pressure.
Tighten the nut to Tightening target torque and hold the torque for Tightening torque duration seconds.
All LEDs are lit when this condition is met.
Relax the torque.
If the parameter Automatic pressure release is ON, the system will release pressure when the torque is relaxed to less than 10 Nm.
If the parameter Automatic pressure release is OFF, release pressure by using de-pressurize button.
When the pressure is released, the OK or NOK result is displayed on the hand controller. In both cases the detailed view shows the recorded pressure/force angle and torque readings.
Aborting
It is always possible to abort an ongoing task but the system pressure must be released before that.
Press de-pressurize button to release pressure.
Press the Back button to exit the tensioning operation.
When aborting tensioning operation during a batch job, the user will get two choice:
Cancel Bolt: if the bolt number is incorrect. The hand controller GUI goes back to screen Position tool on bolt.
Abort Batch: when the tensioning job needs to be paused or stopped.
When running Assembly job, the hand controller GUI goes back to the Tasks menu.
Batch Assembly
A batch is set up to perform a specified number of consecutive tensioning using same tensioning configurations.
On the Home view, go to Tasks > Batch Assembly.
Select a program to run by using the up and down buttons to navigate through the list and the Enter button in the middle to confirm the choice.
The name presented in the list is taken from the Name field under General Settings > Properties tab.
Select one of the two choices as applicable: Tower Section ID or Tower Data.
Scan the flange identifier.
Scan or enter manually the Tower Section ID which is the reference for the specific flange. This identifier is needed to generate the result report since it is used to group the results that belong to a specific flange. For more information about how to use keypad buttons on the hand controller, see section GUI Buttons and Icons.
Scan or enter manually the Tower Data QR code if it is available. This string is a semicolon separated list that includes tower section ID and some additional data added to the results. Hand controller verifies the format of this string and generates error message if it is not approved.
Scan the optional job metadata that is included in the results:
Scan Operator Data
Scan Operator Company
Bolt Data
Flange Location
Operator ID
Operator Data
Operator Company
Press the Forward button to continue.
Enter the total number of bolts on the flange even if the intention is to do a subset of the bolts.
Enter a digit by using the up and down buttons, then press Enter button to confirm. Press Next button to enter the next digit by using the up and down buttons and Enter to confirm the choice.
For more information about how to use keypad buttons on the hand controller, see section GUI Buttons and Icons.
When the total number of bolts on the flange is entered correctly, press the Forward button to enter the summary screen.
The summary screen shows the name of the program to run and the number of bolts.
Press the Forward button to start the first tensioning.
When resuming a previously started batch job, the results of each tensioning appears as green (OK) or red (NOK) on the Position tool on bolt screen.
If the bolt number is not correct, edit it by using the More button.

It is the responsibility of the user to make sure that the bolt number is correct.
Press the Forward button to start tensioning operation, see section Tensioning operation.
Manual Mode
In Manual mode, no process is monitored by the system except for controlling the pressure target, and no results are recorded.
To be able to manually monitor the process, the controller GUI shows the information about the pressure, torque and angle.
The first time Manual mode is run after system startup, the operator must Set Target Pressure by entering the intended target pressure to use. Subsequent manual mode runs will remember the latest used pressure target as long as the system is powered.
The Set Target Pressure screen is populated with the tensioning manual mode configuration parameter Default manual hydraulic pressure.
The target pressure is limited by the lowest of the following:
Max pressure of the pump
Max pressure of the tensioner
Max system hydraulic pressure - the manual mode configuration parameter
Manual Mode Operation
On the Home view, go to Tasks > Manual Mode.
Set the target pressure.
When Position tool on bolt appears, it is possible to change the target pressure by pressing the More button.
Press the Forward button to start Manual mode.
Pressurize by pressing the pressurize button.
Pressurization stops at the target pressure or when the pressurize button is released.
Applied torque on the wrench is visualized both as a white bar and digits.
Registered angle is presented with digits.
When torque starts decreasing, the peak torque is visualized in black, and the present torque in white bar. The peak measurement is presented with digits.
Use the More button to do the following:
Set new pressure target - select Set Target Pressure in the pop-up window.
Clear the registered peak torque and angle.
Moving wrench in counter clockwise direction is registered as negative torque and angle.
To exit manual mode, use the Back button.

Exit manual mode is only possible when pressure is released from the system.
The controller GUI goes back to Tasks menu.
De-tensioning the nut
Turn back the tensioner by 3 mm from the face contact of flange.
Select Manual mode on the hand controller, then set pressure at which bolt was tensioned originally and start building pressure while holding the click wrench with positive force in counterclockwise direction.
When the applied load reaches break opening point, the click wrench moves freely opening the nut. Turn the click wrench 6-7 times its limited window cycle.
Release pressure and check that the bolt is loose.


The max stroke indicator on the puller bar should not be visible while pressuring the tensioner. If visible, stop and adjust the position of the puller bar on bolt so that the max position is not reached until the required pressure is achieved. Otherwise, if done repeatedly, it can physically damage the internal components of the tensioner.

Bolt Service
Bolt service process verifies that the nuts and bolts are in good condition. The nut is loosened to Nut loosening min loosening angle (default value 10 degrees), and then tightened again.
The angle and torque in tightening direction will be displayed as positive values, while the angle and torque in loosening direction as negative values.
On the Home view, go to Tasks > Bolt Service.
Select a program to run by using the up and down buttons to navigate through the list and then the Enter button in the middle to confirm the choice.
The name presented in the list is taken from the Name field under General Settings > Properties tab.
When the message Position tool on bolt appears on the screen, rundown the tensioner straight on top of the bolt.

Make sure that the socket is aligned with the nut.
Press the Forward button on the keypad to start bolt service operation.
Bolt Service Operation
Bolt service operation consists of the following phases:
Installation check
Pressurization phase
Nut loosening
Nut tightening
Aborting can be done anytime during bolt service operation.
When the system waits for the user to take action, a help text appears after a few seconds and it disappears as soon the expected action is detected.
The definition of delta nut rotation is the sum of the nuts rotation: loosening rotation + tightening rotation. For example, if the loosening rotation is −13 degrees, and the tightening rotation is 15 degrees, the total nut rotation is 2. (−13 +15=2)
Installation Check
The purpose of installation check is to create a reference point for the angle measurement.
Press the pressurize button to prevent the tensioner from rotating during installation check.

The pressure may undershoot, especially in the first runs after a long break. In that case press the pressurize button again.

The pressure may overshoot - the system prompts the user to release pressure and try again.
Overshooting can happen due to the parameter Angle reset force, see section Tensioning Parameters.
Turn the nut clockwise to achieve the torque level set in the parameter Installation check torque(default value 20 Nm). Keep the torque for at least Installation check torque duration (default value 1 second).
All 3 LEDs turn green.
Release force on the click wrench.
Turn the nut counter clockwise to achieve the torque level set in the parameter Installation check torque(default value 20 Nm). Keep the torque for at least Installation check torque duration (default value 1 second).
All 3 LEDs turn green.
Release force on the click wrench.
Pressurization Phase
Press and hold the pressurize button.

Do not try to rotate the nut before the target pressure is reached because the nut is fixed to the flange with high force.
Nut Loosening
Keep the pressurize button pressed to allow the system to keep the pressure above the Min bolt tensioning pressure parameter.
The pressure will drop slowly, the system will pressurize before it drops below the minimum pressure.
Loosen the nut to Nut loosening min loosening angle.
If the nut is stuck for some reason, such as corrosion, the system will allow Nut loosening number to attempts, (default value 3), then it prompts the user to tighten the nut again. This will be a NOK result.
An attempt is defined as the applying torque higher than Nut loosening attempt count torque.
All 3 LEDs on the angle row are lit when this condition is met.
If the loosening angle is more than the Nut loosening min loosening angle and the total movement of the nut is within the range between the Min delta nut rotation and Max delta nut rotation, the result is OK.
Nut Tightening
Tighten the nut to Tightening target torque and hold the torque for Tightening torque duration seconds.
All LEDs are lit when this condition is met.
Release force on the click wrench.
If the parameter Automatic pressure release is ON, the system will release pressure when the torque is relaxed to less than 10 Nm.
If the parameter Automatic pressure release is OFF, release pressure by pressing de-pressurize button.
When the pressure is released, the OK or NOK result is displayed on the hand controller. In both cases the detailed view shows the recorded pressure/force angle and torque readings.
If the loosening angle is more than Nut loosening min loosening angle and the total movement of the nut is within the range between the Min delta nut rotation and Max delta nut rotation, the result is OK.
Aborting
It is always possible to abort an ongoing task but the system pressure must be released before that.
Press de-pressurize button to release pressure.
Press the Back button to exit the bolt service operation.
When aborting bolt service operation during a batch job, the user will get two choice:
Cancel Bolt: if the bolt number is incorrect. The hand controller GUI goes back to screen Position tool on bolt.
Abort Batch: when the tensioning job needs to be paused or stopped.
When running Bolt Service job, the hand controller GUI goes back to the Tasks menu.
Batch Bolt Service
On the Home view, go to Tasks > Batch Bolt Service.
Select a program to run by using the up and down buttons to navigate through the list and the Enter button in the middle to confirm the choice.
The name presented in the list is taken from the Name field under General Settings > Properties tab.
Select one of the two choice as applicable: Tower Section ID or Tower Data.
Scan the flange identifier.
Scan or enter manually the Tower Section ID which is the reference for the specific flange. This identifier is needed to generate the result report since it is used to group the results that belong to a specific flange.
For more information about how to use keypad buttons on the hand controller, see section GUI Buttons and Icons.
Scan or enter manually the Tower Data QR code if it is available. This string is a semicolon separated list that includes tower section ID and some additional data added to the results. Hand controller verifies the format of this string and generates error message if it is not approved.
Scan the optional job metadata that is included in the results:
Scan Operator Data
Scan Operator Company
Bolt Data
Flange Location
Operator ID
Operator Data
Operator Company
Press the Forward button to continue.
Enter total number of bolts on the flange even if the intention is to do a subset of the bolts.
For more information about how to use keypad buttons on the hand controller, see section GUI Buttons and Icons.
Press the Forward button to enter the summary screen.
The summary screen shows the name of the program to run and the number of bolts.
Press the Forward button to start the bolt service operation.
When resuming a previously started batch job, the results of each bolt service appears as green (OK) or red (NOK) on the Position tool on bolt screen.
If the bolt number is not correct, edit it by using the More button.

It is the responsibility of the user to make sure that the bolt number is correct.
Press the Forward button to start bolt service operation, see section Bolt Service Operation under Bolt Service.
Working with the Reports Tab
Generate Reports
The reports are generated to a USB flash drive connected to the USB-A connector on the hand controller.
On the Home view, select the Reports tab, then Generate Reports by pressing the Enter button.
To define the date range for generating the report, edit the Start Date and the End Date by using the keypad buttons on the hand controller. If these fields are left empty, the report will include all results in the hand controller.
Press Forward button, then select Start Generation by pressing Enter button or abort by pressing Back button.
A warning text Make sure that a USB flash drive is connected before report generation starts appears.
When the message Report Generated appears o the screen, press the Next button.
Remove the USB flash drive.
Results
Results from batch service jobs can be viewed in the Reports tab. The stored results can be viewed per Tower Section ID for all batch jobs.
The full result of the flange is visualized as a circle.
Green segments for OK results.
Red segments for NOK results.
Active segment is white.
Missing results are grey.
In the Reports tab, select Results.
To define the date range for Results, edit the Start Date and the End Date by using the keypad buttons on the hand controller. If these fields are left empty, all results in the hand controller can be viewed.
Navigate through results by pressing up and down buttons on the keypad
Select the Result to view by pressing the Enter button.
A circle view of the selected Result appears. Each segment represents one bolt in the batch job.
Navigate through the bolt results by using up and down buttons on the keypad to move to the next or to the previous result.
It is possible to navigate to a specific bolt number by using the More button, then enter the bolt number, press the Forward button.
Click the Next button to view details of the chosen bolt.
Working with the Controller Information Tab
The Controller Information menu shows the following information:
Hand controller unit data - serial number
Article number
Ethernet Address
Software version
Software build date
Working with Settings Tab
On the Home view, select the Settings tab to do the following:
Set Time
Set Date
Clear Results
Language
Set Time
Set time in 24-hour time format by using up and down buttons, then press the Next button.
For more information about how to use keypad buttons on the hand controller, see section GUI Buttons and Icons.
Confirm the time with the Forward button when the minute field is active.
To abort it, press the Back button when the hour field is active.
Set Date
Set date in yyyy/mm/dd format by using up and down buttons, then press the Next button.
For more information about how to use keypad buttons on the hand controller, see section GUI Buttons and Icons.
Confirm the date with the Forward button when the day field is active.
To abort it, press the Back button when the field year field is active.
Clear Results
To clear all results stored in the hand controller:
Go to Settings tab, then select Clear Results.
Press the Enter button to confirm, then select Yes in the pop-up window or No to abort.
To avoid problems, it is recommended to clear the results regularly after completed batch jobs and exports. The disk space in the hand controller is not unlimited.
Language
To change the language setting:
Go to Settings tab, then select Language. Press the Enter button to confirm.

The language menu is always last in the list under Home -> Settings to allow navigation to language also when the hand controller is using a language unknown to the operator.
Choose the desired language in the list. Press the Enter button to confirm.
Working with Connected Devices
On the Home view, select the Connected Devices tab to see the data of the connected units.
The main screen also shows information about the following:
Firmware versions
Tensioner size
Puller bar count
Maximum number of puller bar pressurizations
Pump
On the Home view, go to Connected Devices tab.
Select Pump , then press the Enter button to see the following:
Pump details
Pump Custom Identifier
Oil change - Remaining runtime
To see more details press the Enter button.
Pump details
Select Pump details to see information about this connected unit, for example, article number, serial number, hardware version and the following:
Pump motor on time counts the cumber of seconds the motor has been running.
Pump intensifier on time counts the number of seconds the intensifier has been running.
Pump oil pressurization count counts the number of pressurizatons > 75% of max (=>1400 bars) that has passed since the last recorded oil change.
Pump Custom Identifier
Pump Custom Identifier is a field that can be used by the customer to identify the unit with help of an arbitrary ID. The custom ID is stored in the pump and is read by the hand controller at the system startup.
To edit the custom ID, select the Pump Custom Identifier screen by pressing the Enter button.
Press the More button to scan or to manually enter the new custom ID.
Select Scan or Manual Input in the pop-up window for entering the new custom ID.
For Manual input:
Select Save & Exit in the pop-up window, or Reset and Exit to cancel this step.
An event is emitted showing success (Custom ID is set appears).
The characters in the custom identifier must be ASCII characters with values < 128, please refer to an ASCII table.
The new custom ID will not be valid until the next start of the system.
Oil change - Remaining runtime
When the oil and filter change has been completed, confirm the change by selecting Pump -> Oil change - Remaining runtime -> Oil and filter have been changed -> Yes.
The next oil change date will be set one year in the future and the pump motor on time is cleared to 0.
The new date is transferred to the pump and stored, the next oil and filter change date follows the pump and will be displayed in any hand controller that is connected to it.
Tensioner
On the Home view, go to Connected Devices tab.
Select Tensioner, then press the Enter button to see the following:
Tensioner
Puller Bar
Load Cell
Piston
Tensioner Custom identifier
To see more details press the Enter button.

When the list is longer than the screen, use up and down buttons to see the whole list.
Tensioner
Socket Size
Max Pressure
Article Number
Name - this field is set in production
Revision
Serial Number
GUID
Puller bar
Puller bar is an internal wear part that needs to be replaced regularly.
Actual Puller Bar Count shows number of times the puller bar was pressurized, which is >70 % of max pressure (1400 bar).
Max Puller Bar Count shows maximum allowed pressurization, which is >70 % of max pressure (1400 bar).
Remaining Puller Bar Count
Article Number
Serial Number
Assembly Date
Manufacturing Date
Load Cell
Max Pressure
Actual Load Cell count shows the number of pressurizations > 75 % of max (=> 1400 bars).
Article Number
Serial Number
Assembly Date
Manufacturing Date
Piston
Piston Area
Article Number
Serial Number
Assembly Date
Manufacturing Date
Tensioner Custom Identifier
Tensioner Custom Identifier is a field that can be used by the customer to identify the unit with help of an arbitrary ID. The custom ID is stored in the tensioner and is read by the hand controller at the system startup.
To edit the custom ID, select the Tensioner Custom Identifier screen by pressing the Enter button.
Press the More button to scan or to manually enter the new custom ID.
Select Scan or Manual Input in the pop-up window for entering the new custom ID.
For Manual input:
Select Save & Exit in the pop-up window, or Reset and Exit to cancel this step.
An event is emitted showing success (Custom ID is set appears) or failure.
The characters in the custom identifier must be ASCII characters with values < 128, please refer to an ASCII table.
The new custom ID will not be valid until the next start of the system.
Puller Bar Max Warning
When the puller bar counter approaches puller bar max, a warning message Remaining puller bar count, which also appears when starting a tensioning job, appears in the Connected Devices tab.
When the number of remaining tensioning jobs is 500, the warning message Remaining puller bar count: 500 appears. The warning messages continue to appear more frequently when this number comes closer to 0. When the number of remaining tensioning jobs is 0, no more tensioning is allowed. Replace the tensioner to continue the job.
On the controller GUI, select Connected Devices, then select Tensioner and click on Puller Bar to see the following information:
Actual Puller Bar Count
Max Puller Bar Count
Remaining Puller Bar Count
Article number
Serial number
Troubleshooting and Service
This section provides assistance in troubleshooting problems, should they arise, and contains information to help you maintain and service the product.
Troubleshooting and Alarms
The tables below describe different situations, problems and alarms with corresponding possible cause and solutions. The alarms will show an alert with a code on the hand controller for taking corrective actions.
Alarm | Possible cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Pump motor oil temperature high alarm | Oil temperature inside the pump is above the permissible temperature due to different reasons: Continuous working | Leave the pump idle to let it cool down for few minutes. |
Oil quality | Check for contamination. Change the oil. | |
External temperature | Change the oil to appropriate grade. | |
Pump motor oil level low alarm | When the oil level inside the pump is below the minimum level, the system stops. | Top up oil in the pump to resume the work. |
Leakage in the system | Check for leakage in the system, then repair or replace. | |
Pump motor protection alarm | Heavy current or unusual power activity inside the motor. This alarm is triggered for safety of electronics and electrical parts connected to the motor. | Open the small front window on the pump. Reposition the black knob to I position resumes the power supply to the motor. If the error repeats, check the main electrical supply. |
Tool communication disturbance | Overcurrent flowing for an excessive period of time is the most common. This alarm is triggered for the safety of the electronics and electrical parts within the electrical enclosure. | Open the small front window on the pump. Rearm the circuit breaker to resume work. If the breaker keeps tripping within seconds of the rework, stop the work and take corrective actions.
|
An electrical short circuit. | ||
An electrical ground fault. | ||
No pump pressure detected | Motor failure Incorrect phase order in the three-phase connector. | Power off the system and reverse the phases of the power connector. |
Warning | Possible cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Oil change | An oil change is needed. An information message is displayed:
A warning message is displayed:
| Change the oil. Confirm that the oil has ben changed, see Oil change - Remaining runtime, Pump. |
Overtorque | A too high tightening force. | Relax the force on the wrench. |
Overpressure | A too high pressure that can lead to machine damage. | Lower the pressure. |
Problem | Possible cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
Tensioner stuck on the bolt after tensioning | Low charge level of the battery nutrunner. | Replace the battery of the nutrunner with a charged battery. |
No gap between the wall and the tensioner. | Check the wall clearance at the back of the tensioner. If no gap, de-tension the bolt by using the manual mode. | |
Hole alignment, lubrication and bolt threads. | Check also the hole alignment, lubrication and bolt threads. If any doubts, change the bolt and try again. | |
Tensioner does not run down on bolt | Bolt threads are damaged. | Replace the bolt. |
Bolt threads are not lubricated. | Lubricate bolt threads. | |
Debris inside the tensioner threads. | Remove debris from the threads with a wire brush. | |
Bolt protrusion exceeds the maximum limit. | Adjust the protrusion by loosening the bolt so that it does not exceed the maximum limit. | |
Pressure not building over 200 bar in the pump | Leakage on the pump. | Check for leakage on the pump or in the hydraulic line of the system. Check the oil level. Top up with oil if too low. Send the pump for maintenance or repair if the problem persists. |
Wrong grade of oil. | Make sure to use the right grade of oil. | |
Hard to disconnect hydraulic line coupler from the pump | The nipple on the hose is worn out. | Change nipples on the hose and tensioner as soon as it becomes sticky and harder to disconnect. |
Troubleshooting the Barcode Reader
If the hand controller does not display any strings when using the barcode reader, scan the following barcodes to make sure that it is configured correctly.

Enable Picklist Mode Always 
USB HID Keyboard
Reference
In this section, you can find miscellaneous useful information.
Terms and Definitions
Term | Synonym | Definition | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
batch | multiple tensioning using the same tensioning program and socket | ||
controller GUI | Graphical User Interface | hand controller user interface used to operate the system | |
event | status signals from hand controller or connected devices | ||
final angle | actual measured angle value at the end of the tensioning process | ||
final torque | actual measured torque value at the end of the tensioning process | ||
final pressure | actual measured pressure value at the end of the tensioning process | ||
GUI | Graphical User Interface | graphical user interface made up of interactive graphical elements such as windows, icons and symbols on a display | |
IAM | Intelligent Application Module | hand controller module containing production data | |
Tensioning program | Parameter set | configuration of parameters and values to control and monitor a single tensioning action, and to store the tensioning result | the target is expressed as pressure, torque or angle. |
target | desired result of a tensioning | The target is expressed in torque or angle. | |
target angle | desired angle value at the end of the tensioning process measured from a reference point | ||
target torque | desired torque value at the end of the tensioning process | ||
web GUI | user interface to controller through web browser window from a remote computer | ||
virtual station | virtual controller | software abstraction of a physical controller | A controller can be part of only one tensioning system. |
Third Party Licenses
List of Third-Party Licenses
Power Focus controllers incorporate third-party components whose licenses require us to publish copies of the licensing language and/or copyright notices. In compliance with those requirements, here are copies of the licenses. Please, click on any of the licenses below to show a copy of the license text.
Software | Version | Licenses (SPDX) |
|---|---|---|
alsa-conf | 1.1.5 | |
atftpd | 0.7.4 | |
barebox | 2021.01.0 | |
base-files | 3.0.14 | |
base-files-px2-base | 1.0 |
|
bash | 4.4.12 | |
bash-completion | 2.7 | |
bats-core | git | |
bind-libs | 9.11.22 | |
bluez5 | 5.54 | |
boost | 1.64.0 | |
busybox | 1.27.2 | |
bzip2 | 1.0.6 | |
ca-certificates | 20170717 | |
cppunit | 1.13.2 | |
curl | 7.61.0 | |
db | 1:5.3.28 | |
db-dev | 1:5.3.28 | |
dbus-1 | 1.12.2 | |
dhcp | 4.4.2 | |
dnsmasq | 2.85 | |
dosfstools | 4.1 | |
e2fsprogs | 1.43.8 | |
ecryptfs-tools | 1.0 | |
eudev | 3.2.5 | |
evtest | 1.33+0+ab140a2dab | |
examples | 1.0 | |
expect | 5.45.4 | |
fcgi | 2.4.0 | |
file | 5.32 | |
finit | 3.1 | |
flatbuffers | 1.9.0 | |
fontconfig-utils | 2.13.92 | |
gcc | 7.3.0 | |
gdbm | 1.19 | |
gdbserver | 8.0.1 | |
glibc-gconv | 2.27 | |
glibc-gconv-utf-16 | 2.27 | |
grep | 3.1 | |
groupexec | 0.0.1 |
|
hicolor-icon-theme | 0.17 | |
hostapd | 2.6 | |
html5-boilerplate | 6.0+20171125 | |
htop | 2.1.0 | |
i2c-tools | 4.1 | |
icu | 66.1 | |
init-ifupdown | 1.0 |
|
iperf3 | 3.2 | |
iproute2 | 4.14.1 | |
iptables | 1.6.2 | |
ipwatchd | 1.2 | |
iw | 4.14 | |
jq | 1.5 | |
kbd | 2.0.4 | |
kernel-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-devicetree | 4.14 | |
kernel-image-zimage-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-arptable-filter-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-arp-tables-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-binfmt-misc-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-br-netfilter-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-cdc-eem-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-crc7-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-crc-itu-t-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-crypto-engine-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-echainiv-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-hostap-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-i2c-algo-pca-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-i2c-algo-pcf-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-imx-rpmsg-pingpong-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-imx-rpmsg-tty-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-iptable-filter-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-iptable-mangle-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-iptable-raw-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-ip-tables-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-ipt-reject-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-isofs-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-lib80211-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-lib80211-crypt-ccmp-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-lib80211-crypt-tkip-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-lib80211-crypt-wep-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-libcrc32c-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-msdos-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-conntrack-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-conntrack-ipv4-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-conntrack-netlink-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-defrag-ipv4-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-log-common-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-log-ipv4-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-log-ipv6-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nfnetlink-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nfnetlink-log-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nfnetlink-queue-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nf-reject-ipv4-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-nls-iso8859-15-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-onebox-bt-gpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-onebox-bt-nongpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-onebox-common-gpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-onebox-gpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-onebox-nongpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-onebox-wlan-gpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-onebox-wlan-nongpl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-pegasus-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-r8152-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-rndis-host-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-rtl8150-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-modules | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-udf-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-virtio-crypto-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-wlan-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-acl-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-aes-cmac-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-ccmp-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-scan-sta-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-tkip-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-wep-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-wlan-xauth-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 1.0 | |
kernel-module-x-tables-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-comment-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-connmark-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-conntrack-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-limit-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-log-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-mac-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-mark-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-multiport-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-pkttype-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-state-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
kernel-module-xt-tcpudp-4.14.115-atlas-sxb | 4.14 | |
keyinput-cli | 1.0 | |
keyutils | 1.5.9 | |
kmod | 25+git0+aca4eca103 | |
libacl1 | 2.2.52 | |
libaio1 | 0.3.110 | |
libanybus1 | 1.1 |
|
libanybus2-3 | 3.6.1 | |
libarchive | 3.3.2 | |
libasound2 | 1.1.5 | |
libatk-1.0-0 | 2.36.0 | |
libatk-bridge-2.0-0 | 2.34.2 | |
libatspi0 | 2.36.0 | |
libattr1 | 2.4.47 | |
libblkid1 | 2.32.1 | |
libboost | 1.64.0 | |
libbsd0 | 0.8.7 | |
libbz2-1 | 1.0.6 | |
libc6 | 2.27 | |
libcairo2 | 1.16.0 | |
libcap2 | 2.25 | |
libcidn1 | 2.27 | |
libcrypto1.1 | 1.1.1f | |
libdrm2 | 2.4.100 | |
libdt-utils0 | 2017.03.0 | |
libdt-utils-barebox-state | 2017.03.0 | |
libe2p2 | 1.43.8 | |
libelf1 | 0.170 | |
libestr0 | 0.1.10 | |
libevdev | 1.5.8 | |
libexpat1 | 2.2.5 | |
libext2fs2 | 1.43.8 | |
libfastjson4 | 0.99.4 | |
libfdisk1 | 2.32.1 | |
libffi6 | 3.2.1 | |
libffi-dev | 3.2.1 | |
libflac8 | 1.3.2 | |
libfontconfig1 | 2.13.92 | |
libform5 | 6.0+20171125 | |
libformw5 | 6.0+20171125 | |
libfreetype6 | 2.10.1 | |
libfruit3 | 3.4.0+git0+ece0f7218c | |
libgcrypt | 1.8.2 | |
libglib-2.0-0 | 1:2.54.3 | |
libgmp10 | 6.1.2 | |
libgnutls30 | 3.6.1 | |
libgpg-error0 | 1.27 | |
libgpiod1 | 1.0.1 | |
libgpiod-tools | 1.0.1 | |
libgudev-1.0-0 | 232 | |
libharfbuzz0 | 1.7.5 | |
libiio0 | 0.21+git0+565bf68ecc | |
libinput10 | 1.16.1 | |
libite5 | 2.2.0+git0+ef04307b4a | |
libjpeg62 | 1:1.5.3 | |
libjson-glib-1.0-0 | 1.4.2 | |
libjson-spirit4 | 4.08 | |
libkmod2 | 25+git0+aca4eca103 | |
liblogging | 1.0.5 | |
libluabind0 | git | |
liblzma5 | 5.2.3 | |
liblzo2-2 | 2.10 | |
libmbim | 1.14.0 | |
libminizip1 | 1.2.8 | |
libmnl0 | 1.0.4 | |
libmodbus5 | 3.1.4 | |
libmount1 | 2.32.1 | |
libnet9 | 1.2 | |
libnl-3-200 | 1:3.4.0 | |
libnl-genl-3-200 | 1:3.4.0 | |
libogg0 | 1.3.3 | |
libonig2 | 5.9.6 | |
libopkg1 | 1:0.3.6 | |
libpcap1 | 1.8.1 | |
libpcre1 | 8.41 | |
libpixman-1-0 | 1:0.34.0 | |
libpng16-16 | 1.6.34 | |
libpopt0 | 1.16 | |
libprotobuf15 | 3.5.1+git0+106ffc04be | |
libpugixml1 | 1.10 | |
libpx2dbus1 | 1.0.0 |
|
libpython2.7-1.0 | 2.7.15 | |
librcf2 | 2.2.0.0 | |
libreadline7 | 7.0 | |
libsmartcols1 | 2.32.1 | |
libsolv0 | 0.6.33 | |
libtcl8.6-0 | 8.6.8 | |
libtic5 | 6.0+20171125 | |
libticw5 | 6.0+20171125 | |
libtinfo5 | 6.0+20171125 | |
libtinyxml2.6.2 | 2.6.2 | |
libts0 | 1.22 | |
libubootenv0 | 0.3.2 | |
libubootenv-bin | 0.3.2 | |
libudev1 | 3.2.5 | |
libuev2 | 2.3.1+git0+8d07cc616e | |
libunistring2 | 0.9.9 | |
libusb-1.0-0 | 1.0.21 | |
libuuid1 | 2.32.1 | |
libweston-8 | 8.0.0 | |
libwrap0 | 7.6 | |
libx11-compose-data | 1.6.5 | |
libxkbcommon0 | 0.8.0 | |
libxml2 | 2.9.7 | |
libxslt | 1.1.32 | |
libz1 | 1.2.11 | |
libz-dev | 1.2.11 | |
lighttpd | 1.4.59 | |
linux-firmware-imx-sdma-imx7d | 1:0.0+git0+d114732723 |
|
linux-firmware-imx-sdma-license | 1:0.0+git0+d114732723 |
|
linux-libc-headers-dev | 4.15.7 | |
logrotate | 3.13.0 | |
lua | 5.1.5 | |
lz4 | 1:1.7.4 | |
lzop | 1.03 | |
memlog | 2.0 | |
memprof | 0.2.0 | |
mesa | 2:17.3.8 | |
mg | 20170401 | |
minizip | 1.2.8 | |
mmc-utils | 0.1 | |
mtdev | 1.1.6 | |
mtd-utils | 2.0.1+0+9c6173559f | |
nano | 2.9.3 | |
ncurses | 6.0+20171125 | |
netbase | 1:5.4 | |
netcat-openbsd | 1.105 | |
nettle | 3.4 | |
nspr | 4.19 | |
nss | 3.35 | |
ntp | 4.2.8p15 | |
openssh | 8.9p1 | |
openssl | 1.1.1f | |
opkg | 1:0.3.6 | |
os-release | 1.0 | |
pango | 1.40.14 | |
parted | 3.2 | |
partitions | 1.0 |
|
pfmfonts | 0.0.1 |
|
pfmtool | 1.0 |
|
pfmversion | 7.35.1 |
|
pm-utils | 1.4.1 | |
poco | 1.11.1 | |
pointercal | 0.0 | |
procps | 3.3.12 | |
pwr-manager | 1.0 |
|
px2hal | 0.0.1 |
|
px2initsxb | 1.0 |
|
px2network | 1.0 |
|
px2users-logger | 1.0 |
|
px2users-pxtv | 1.0 |
|
px2users-reader | 1.0 |
|
px2w | 0.0.1 |
|
px2watchdog | 1.0 |
|
python | 2.7.15 | |
qt5 | 5.10.1+git0+6c6ace9d23 | |
rauc | 1.0 | |
redpine | 1.0 | |
rng-tools | 5 | |
rsync | 3.2.3 | |
rsyslog | 8.29.0 | |
shadow-base | 4.2.1 | |
shadow-securetty | 4.2.1 | |
shared-mime-info | 1.9 | |
sqlite3 | 3:3.22.0 | |
squashfs-tools | 4.3+gitr0+9c1db6d13a | |
ssh-keys | 6.0 |
|
st-load | 1.0 | |
stm32flash | 0.6 | |
strace | 4.20 | |
stress-ng | 0.09.14 | |
sysstat | 11.7.1 | |
sysvinit | 2.88dsf | |
tcf-agent | 1.4.0+git0+2dddd5f440 | |
tcl | 8.6.8 | |
tcpdump | 4.9.2 | |
tslib | 1.22 | |
ttc-noto-cjk-sans-otc | 2.004 | |
ttf-arimo | 1.0 | |
tzdata | 2018i | |
udev-rules-imx | 1.0 |
|
unzip | 1:6.0 | |
upower | 0.99.11 | |
usbutils | 009 | |
util-linux | 2.32.1 | |
wayland | 1.18.0 | |
weston | 8.0.0 | |
wireless-regdb-static | 2021.04.21 | |
wireless-tools | 1:30.pre9 | |
wpa-supplicant | 2.9 | |
xerces-c | 2.7.0 | |
xkeyboard-config | 2.22 | |
yaml-cpp | 0.6.2 | |
zip | 3.0 | |
lwip | 2.1.2 | |
FreeRTOS | 7.1.0 |
Output Signals
Tool Enabled - 159
Tool Enabled is an output signal which is activated when the tool is not externally disabled by any of the following signals:
20002 - Lock Tightening
20003 - Lock Loosening
20004 - Lock Tool Active High
20033 - Line Control Lock
20018 - Open Protocol Lock
20020 - Fieldbus Lock Tightening
20021 - Fieldbus Lock Loosening
20040 - Soft PLC Lock Tightening
20041 - Soft PLC Lock Loosening
20061 - Lock Tool Active Low
Name in SoftPLC: TOOL_ENABLED
Signal Type | Value Type | Size Min [bit] | Size Max [bit] |
|---|---|---|---|
State | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
Devices
Fieldbus: TRUE
Indicator Box: TRUE
Internal I/O: TRUE
Operator Panel: TRUE
Tool Functions: TRUE
ST Selector: FALSE
Stacklight: TRUE
TLS Tag: TRUE
I/O Expander: TRUE
Open Protocol Disconnected - 95
If Open Protocol is set to off in the Virtual Station, "Open Protocol Disconnected" signal is set to False.
If Open Protocol is turned on in the Virtual Station the "Open Protocol Disconnected" signal is set to True.
When at least one client (several Open Protocol clients can connect to the same Virtual Station) is connected the "Open Protocol Disconnected" signal is set to False.
Name in SoftPLC: OPEN_PROTOCOL_DISCONNECTED
Converter | Signal Type | Value Type | Size Min [bit] | Size Max [bit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Standard | State | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
Invert | State | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
To avoid duplicating signals, it is possible to define Value Converters.
Converters are used to support more than one representation of the same signal (for example Angle/Torque Status can both be represented bitwise or as a status character).
Devices
Fieldbus: TRUE
Indicator Box: TRUE
Internal I/O: TRUE
Operator Panel: TRUE
Tool Functions: TRUE
ST Selector: FALSE
Stacklight: TRUE
TLS Tag: TRUE
I/O Expander: TRUE
Input/Output Signals
Clear Results - 39
Clears status of other signals set to next tightening.
Name in SoftPLC: CLEAR_RESULTS
Signal Type | Value Type | Size Min [bit] | Size Max [bit] |
|---|---|---|---|
Event | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
Devices
Fieldbus: TRUE
Indicator Box: FALSE
Internal I/O: TRUE
Operator Panel: TRUE
Tool Functions: FALSE
ST Selector: FALSE
Stacklight: TRUE
TLS Tag: FALSE
I/O Expander: TRUE
Disable Open Protocol Commands - 10060
Disables the possibility to send commands over Open Protocol to the Virtual Station.
Name in SoftPLC: DISABLE_OPEN_PRTCOL_CMDS
Converter | Signal Type | Value Type | Size Min [bit] | Size Max [bit] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Standard | State | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
Invert | State | Boolean | 1 | 1 |
To avoid duplicating signals, it is possible to define Value Converters.
Converters are used to support more than one representation of the same signal (for example Angle/Torque Status can both be represented bitwise or as a status character).
Devices
Fieldbus: TRUE
Indicator Box: TRUE
Internal I/O: TRUE
Operator Panel: TRUE
Tool Functions: TRUE
ST Selector: FALSE
Stacklight: TRUE
TLS Tag: TRUE
I/O Expander: TRUE


















